ISP uses communication interfaces for programming, and the boot code is written by the manufacturer and cannot be changed.

IAP (In-Application Programming) refers to the ability of an MCU to obtain new code and reprogram itself, allowing a program to change the program. In application programming (IAP), the user’s application code erases/programs the internal Flash memory. A typical application of this method is to use a small piece of code to implement program downloading. In fact, the ISP function of the microcontroller is realized through IAP technology, meaning that a small boot program is already embedded in the chip before it leaves the factory. When powered on, the chip starts running this program. When it detects a download request from the host computer, it communicates with the host and downloads data to the data storage area, thus enabling firmware upgrades.
Follow our official account and reply with “IAP” to obtain the following official resources.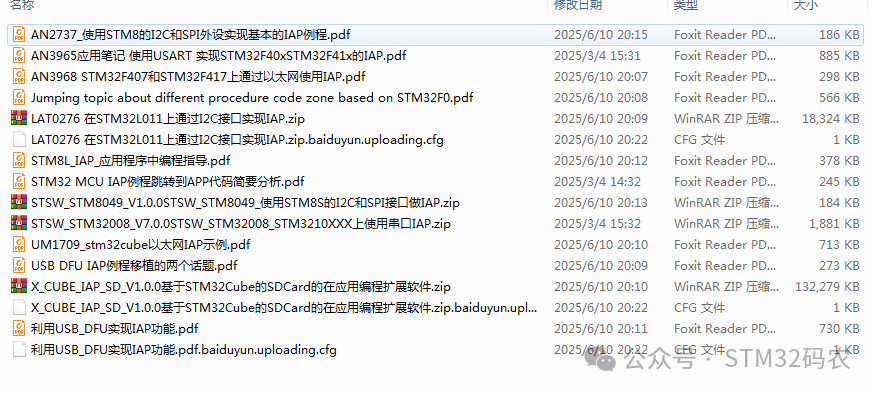 The main resources include:(1)AN2737: Basic IAP example using I2C and SPI peripherals with STM8(2)AN3965 Application Note: Implementing IAP for STM32F40x and STM32F41x using USART(3)AN3968: Using IAP over Ethernet on STM32F407 and STM32F417(4)Jumping topic about different procedure code zones based on STM32F0(5)LAT0276: Implementing IAP via I2C interface on STM32L011.zip(6)Programming guide in STM8L_IAP application.pdf(7)Brief analysis of jumping to APP code in STM32 MCU IAP example(8)STSW_STM8049_V1.0.0: Using I2C and SPI interfaces for IAP with STM8S(9)STSW_STM32008_V7.0.0: Using serial port IAP on STM3210XXX(10)UM1709: STM32Cube Ethernet IAP example(11)Two topics on porting USB DFU IAP examples(12)X_CUBE_IAP_SD_V1.0.0: Application programming extension software for SDCard based on STM32Cube(13)Implementing IAP functionality using USB_DFU
The main resources include:(1)AN2737: Basic IAP example using I2C and SPI peripherals with STM8(2)AN3965 Application Note: Implementing IAP for STM32F40x and STM32F41x using USART(3)AN3968: Using IAP over Ethernet on STM32F407 and STM32F417(4)Jumping topic about different procedure code zones based on STM32F0(5)LAT0276: Implementing IAP via I2C interface on STM32L011.zip(6)Programming guide in STM8L_IAP application.pdf(7)Brief analysis of jumping to APP code in STM32 MCU IAP example(8)STSW_STM8049_V1.0.0: Using I2C and SPI interfaces for IAP with STM8S(9)STSW_STM32008_V7.0.0: Using serial port IAP on STM3210XXX(10)UM1709: STM32Cube Ethernet IAP example(11)Two topics on porting USB DFU IAP examples(12)X_CUBE_IAP_SD_V1.0.0: Application programming extension software for SDCard based on STM32Cube(13)Implementing IAP functionality using USB_DFU