string.h is one of the most commonly used libraries in C language, which can be broadly divided into memory operations and string operations. This article will detail all the functions in
<span>memory operations</span>. 🌟

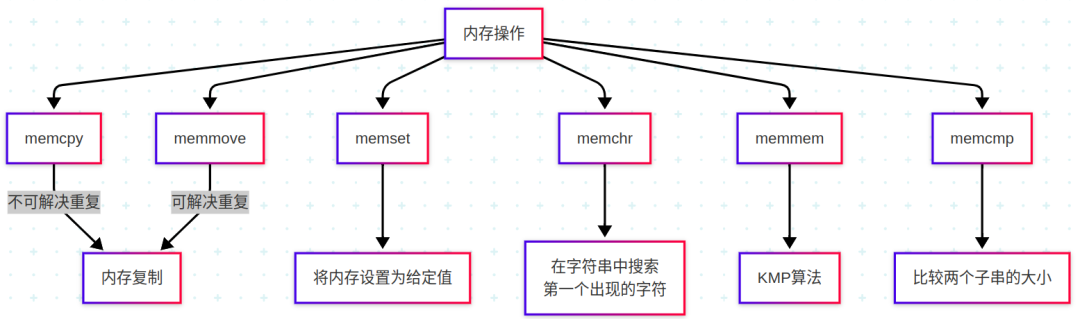
1. Memory Operations
-
<span>memcpy</span> - Function: Copies n bytes from the source address to the destination address.
- Prototype:
<span>extern void *memcpy (void *__restrict __dest, const void *__restrict __src, size_t __n);</span> - Parameters:
<span>From left to right: destination address, source address, size of memory block to copy</span>. - Return Value: Returns the pointer to the destination address regardless of success or failure (for subsequent use).
- No Overlapping Memory Handling: If the source and destination addresses overlap, data will be overwritten, leading to errors.
-
<span>memmove</span>Note: Generally, when the source and destination addresses overlap, there is a difference; otherwise, they are the same.
- Function: Copies n bytes from the source address to the destination address, automatically handling overlapping addresses without causing data overwrite.
- Prototype:
<span>extern void *memmove(void *__dest, const void *__src, size_t __n);</span> - Parameters:
<span>From left to right: destination address, source address, size of memory block to copy</span>. - Return Value: Returns the pointer to the destination address regardless of success or failure (for subsequent use).
- Overlapping Memory Handling: If the source and destination addresses overlap, memory will be automatically adjusted to prevent overwriting.
-
<span>memset</span> - Function: Sets the value of n bytes in the memory area to a given value.
- Prototype:
<span>extern void *memset (void *__s, int __c, size_t __n);</span> - Parameters:
<span>From left to right: destination address, value to set, size of memory block to set</span> - Return Value: Returns the pointer to the destination address regardless of success or failure (for subsequent use).
-
<span>memchr</span> - Function: Searches for the first occurrence of character c in the memory area pointed to, which is n bytes in size, and returns the pointer to this position.
- Prototype:
<span>void *memchr(const void *str, int c, size_t n);</span> - Parameters:
<span>From left to right: search address, value to search for, byte range to search</span> - Return Value: Address of the found value.
-
<span>memmem</span> - Function: A function to find a substring (needle) in a memory block (haystack).
- Prototype:
<span>void *memmem (const void *__haystack, size_t __haystacklen, const void *__needle, size_t __needlelen)</span> - Parameters:
<span>From left to right: total string, total character length, string to search for, length of string to search for</span> - Return Value: Returns the pointer to the matched substring, NULL if not matched.
-
<span>memcmp</span> - Function: Compares two substrings A and B using memcmp(A,B), returning 0 if equal, negative if A < B, and positive if A > B
<span>(essentially A-B)</span> - Prototype:
<span>extern int memcmp (const void *__s1, const void *__s2, size_t __n);</span> - Parameters:
<span>From left to right: two strings to compare and their length</span> - Return Value: -1, 0, 1 indicating the equality of the two substrings.
2. Testing
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define __USE_GNU /* Enable GNU extensions */
#define MEMCPY
#define MEMMOVE
#define MEMSET_MEMMOVE
#define MEMSET
#define MEMCHR
#define MEMNCHR
#define MEMMEM
#define MEMCMP
/**
* func descp: Custom function to search for the nth occurrence of a character
*/
int memnchr(char *dest, int ch, size_t n, size_t index)
{
char *originPos = dest;
if (n 0 || index 0)
{
return -1;
}
size_t found_count = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
char *pointer = memchr(dest, ch, n - i);
if (pointer != NULL)
{
found_count++;
if (found_count == index)
{
printf("Found the %zu-th occurrence of character %c at position %zu\n", index, (char)ch, pointer - originPos + 1);
return pointer - originPos + 1;
}
// Update pointer position
dest = pointer + 1;
i = 0;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
printf("No corresponding word found.\n");
return -1;
}
int main()
{
char *str = "Hello, World!";
printf("Test MEMCPY:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMCPY
{
// Destination
char dest[20];
memcpy(dest, str + 1, 20);
// Add a null character at the end of the destination
dest[20] = '\0';
printf("Copied string: %s\n", dest);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
printf("%c--%d\n", dest[i], i);
}
dest[4] = '\0';
/**
* data descp: printf will keep printing until it encounters \0, so we need to add a null character at the end of the destination, otherwise it will keep printing to the end of memory.
*/
printf("%s\n", dest);
}
#endif
printf("\nTest MEMMOVE:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMMOVE
{
char dest[20];
memmove(dest, str + 1, strlen(dest));
// Add a null character at the end of the destination
dest[20] = '\0';
printf("Copied string: %s\n", dest);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
printf("%c--%d\n", dest[i], i);
}
dest[4] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", dest);
}
#endif
printf("\nTest MEMSET:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMSET
{
char dest[20] = "1234";
memset(dest + 4, 'A', 16);
// Add a null character at the end of the destination
dest[19] = '\0';
printf("Copied string: %s\n", dest);
printf("Copied string: %s\n", (char *)memset(dest + 4, 'A', 16));
}
#endif
printf("\nTest MEMCHR:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMCHR
{
char dest[20] = "0000000001234";
char *ch1 = (char *)memchr(dest, '1', strlen(dest));
// Add a null character at the end of the destination
if (ch1 != NULL)
{
printf("The first character %c is at position %ld\n", *ch1, ch1 - dest);
}
else
{
printf("No corresponding word found.\n");
}
}
#endif
printf("\nTest MEMNCHR:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMNCHR
{
/**
* func descp: Custom function to search for the nth occurrence of a character
*/
char dest[20] = "000011100001234";
int pos = memnchr(dest, '0', strlen(dest), 8);
}
#endif
printf("\nTest MEMMEM:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMMEM
{
char str1[] = "This is a sample string";
char str2[] = "sample";
char *ptr = memmem(str1, strlen(str1), str2, strlen(str2));
if (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%c\n", *ptr);
printf("Found substring '%s' at position %ld\n", str2, ptr - str1);
}
else
{
printf("Substring '%s' not found in the string\n", str2);
}
}
#endif
printf("\nTest MEMCMP:\n\n");
#ifdef MEMCMP
{
char str1[] = "ABC";
char str2[] = "ABDE";
int cmp = memcmp(str1, str2, 3);
printf("%d\n", cmp);
if (cmp > 0)
{
printf("str1 > str2\n");
}
else if (cmp < 0)
{
printf("str1 < str2\n");
}
else
{
printf("str1 = str2\n");
}
}
#endif
return 0;
}
Results
Test MEMCPY:
Copied string: ello, World!
e--0
l--1
l--2
o--3
,--4
--5
W--6
o--7
r--8
l--9
d--10
!--11
--12
T--13
e--14
s--15
t--16
--17
M--18
E--19
ello
Test MEMMOVE:
Copied string: ello
e--0
l--1
l--2
o--3
--4
--5
W--6
o--7
r--8
l--9
d--10
!--11
--12
T--13
e--14
s--15
t--16
--17
M--18
E--19
ello
Test MEMSET:
Copied string: 1234AAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
Copied string: AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
Test MEMCHR:
The first character 1 is at position 9
Test MEMNCHR:
Found the 8-th occurrence of character 0 at position 11
Test MEMMEM:
Found substring 'sample' at position 10
Test MEMCMP:
-1
str1<str2