Input Events to State Machine
#include "stdio.h"
#define EXECUTE_VOID(func) {if((func)!=NULL) (func());}
typedef void (*select_machine_t)(void);
typedef enum _event_index{ event_index_1 = 0, event_index_2, event_index_3, event_index_end} event_index_e;
typedef enum _status_index{ status_index_1 = 0, status_index_2, status_index_end} status_index_e;
void machine_1(void);void machine_2(void);void machine_3(void);void machine_4(void);
select_machine_t select_machine[event_index_end][status_index_end] = { {machine_1, machine_2}, {NULL, machine_3}, {machine_4, NULL}};
void machine_1(void){ printf("machine_1\r\n");}
void machine_2(void){ printf("machine_2\r\n");}
void machine_3(void){ printf("machine_3\r\n");}
void machine_4(void){ printf("machine_4\r\n");}
int main(void){ EXECUTE_VOID(select_machine[0][1]);} Corresponding:
(1)Condition A: status_index_e(2)Condition B: event_index_e
(3)Switch:
EXECUTE_VOID(select_machine[0][1] ); When an external event occurs (for example, a key input), the current real-time state is introduced through a global structure variable (the most common method in C language), directing various state machines based on conditions. The implementation here is through a two-dimensional array where two indices represent two conditions, and the intersection of these two conditions is the specific state machine.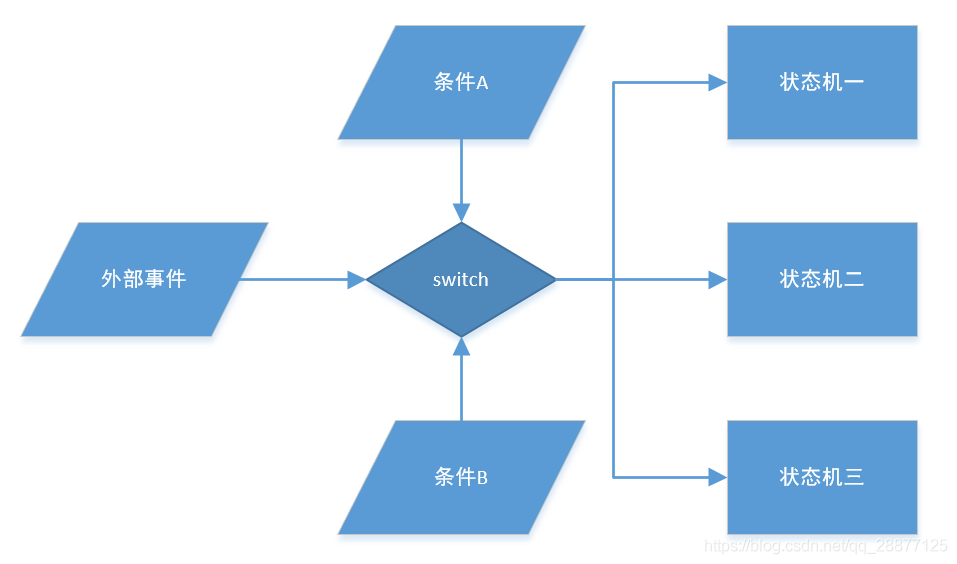
State Machine to Procedural Programming
The above implementation is “Input External Events >>> Directing to >>> State Machine” So how to implement “State Machine >>> Execute >>> Specific Operations”? The state machine has a fixed execution flow (of course, there are also branches that execute different processes based on conditions), and these processes are very definite execution sequences. Experience in the development process reflects: it is about the precise and complete analysis of all execution flows, and then listing them all. “Listing them all” can be represented in two ways in the program:1. Listing all execution flows in the form of “empty functions”.2. Listing all execution flows in the form of “function pointers”: Benefit 1: The software framework can be written out, and the specific logical flow is already prepared. Benefit 2: The specific function interfaces can be left empty (NULL), and once the function is written, the function name can be assigned to it (sys_api_func* = you_func;). Benefit 3:
Higher generality and stronger logic.
void (sys_api_func1)(void);
void (sys_api_func2)(void);
void (sys_api_func3)(void);
...
void sys_api_init(void){ sys_api_func1 = NULL; // Assign NULL if the implementation function is not yet written
sys_api_func2 = NULL;
sys_api_func3 = NULL;
...}
// State Machine 1
void machine_1(void){ execute_api_void(sys_api_func1); // State Machine: Step One
execute_api_void(sys_api_func2); // State Machine: Step Two
... // State Machine: Steps....}Link: https://liefyuan.blog.csdn.net/article/