Click the blue text to follow us

1. Concept of Microcontroller
Microcontroller—Single Chip MicroComputer (SCMC)
Microcontroller Unit (MCU)
Embedded MicroController Unit (EMCU)
MicroComputer Development System (MDS)
In Circuit Emulator (ICE)
2. Two Branches of Microcomputers
-
One is developing towards high-speed, large-capacity, and high-performance high-end microcomputers

-
The other is developing towards stable, reliable, small-sized, and low-cost microcontrollers (mainly used for control)

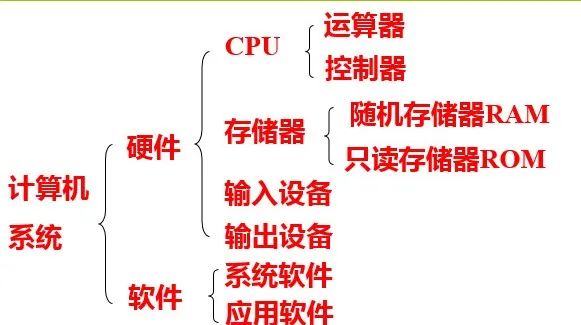
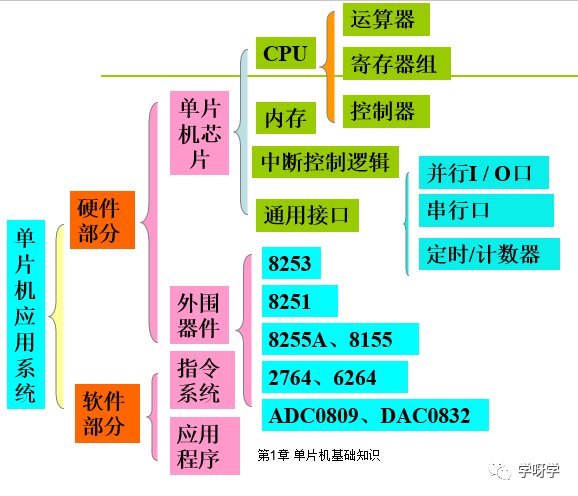
3. Composition of Computer System
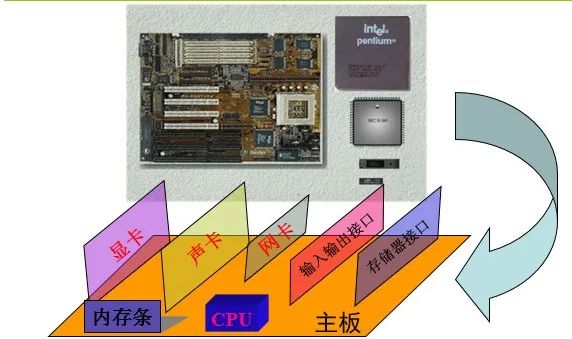
4. Hardware Composition of Microcomputer
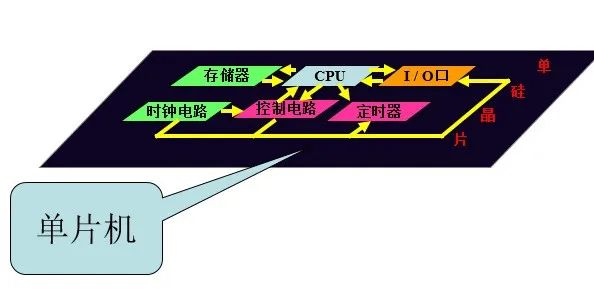
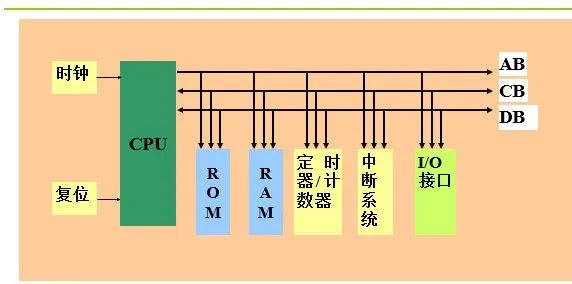
Microcontroller System Structure
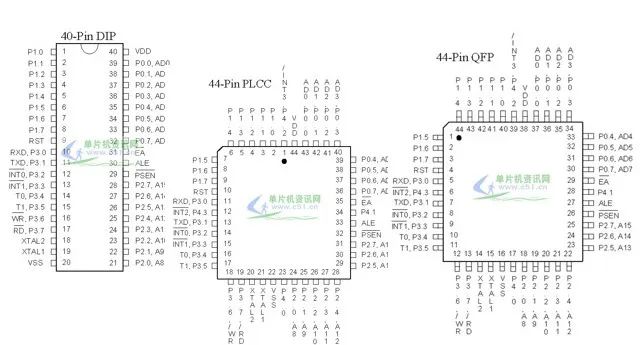
Package Types of MCS51 Microcontroller
(2) Functions:
Same: PC: Data computation, collection, processing, storage, transmission;
Microcontroller: Controls (or is controlled by) peripherals.
Different: General-purpose computers excel in data computation, collection, processing, storage, and transmission;
Microcontrollers specialize in measurement and control, often embedded in instruments/devices/systems to achieve intelligent effects.
(3) Application Characteristics:
Personal computers (microcomputers): Large size, high power consumption, high price, relatively fixed purpose, belong to general-purpose computers. Easy to learn and use, but when used for control, special interface cards must be made or purchased, and specialized application software must be developed.
Microcontroller: Dedicated computer.
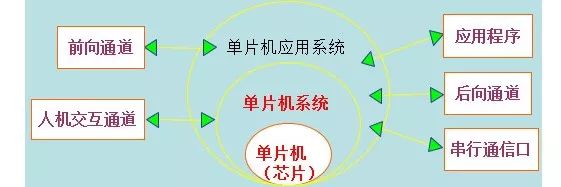
7. Microcontroller System
2. Development and Application of Microcontroller
1. Development of Microcontroller
-
Initial Stage of Microcontroller Development (1971-1976)
Mainly focuses on 4-bit and 8-bit microcontroller early products. At this time, the manufacturing technology of microcontrollers was backward, the integration level was low, and they were mainly used in instruments, meters, consumer electronics, and calculators.
-
Development Stage of Microcontroller (1976-1980)
At this time, various 8-bit microcontrollers appeared, with Intel’s MCS-48 series microcontroller as a representative. This type of microcontroller adopted a single-chip structure, integrating the CPU and peripheral circuits onto one chip, using an 8-bit CPU, multiple parallel I/O ports, and an 8-bit timer/counter, but without a serial port. Its emergence marked the beginning of the separation between microcontrollers and general-purpose CPUs, forming new industrial controllers.
-
Mature Stage of 8-bit Microcontroller (1980-1983)
This stage is represented by Intel’s MCS-51 series microcontrollers, producing various high-performance microcontrollers. These microcontrollers integrated full-duplex serial communication ports and multiple 16-bit timers/counters. Storage capacity further expanded, and on-chip resources became richer, leading to widespread application.
-
High-Performance Microcontroller Development Stage (After 1983)
After Intel launched the 16-bit MCS-96 microcontroller in 1983, major manufacturers also introduced high-performance microcontrollers, with some reaching 32 bits. However, during this stage, 8-bit microcontrollers still had a large market application.
Divided by microcontroller bit:
-
4-bit Microcontroller Stage
4-bit microcontrollers are mainly used in household appliances, electronic toys, etc.
-
8-bit Microcontroller Stage
8-bit microcontrollers are widely used in industrial control, intelligent interfaces, instruments, and meters due to their strong functionality.
-
16-bit Microcontroller Stage
16-bit microcontrollers can be used in high-speed complex control systems.
-
32-bit Microcontroller
In recent years, various computer manufacturers have entered the development and production stage of higher-performance 32-bit microcontrollers. Due to the not-so-urgent demand for 32-bit microcontrollers in the control field, their application is not very widespread.
Currently, the mainstream model widely used is the 80C51 series 8-bit microcontroller.
2. 80C51 Series Microcontroller
Today’s 80C51 is not limited to Intel, but refers to all models compatible with 80C51 based on the 8051 core.
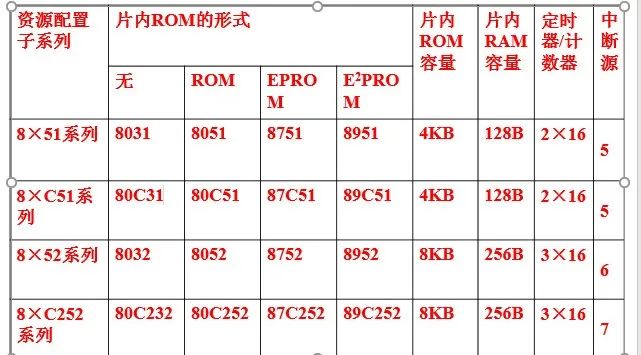
Application Scope:
-
Mechatronics -
Industrial Control: CNC Machine Tools, Industrial Robots, Temperature Control -
Instruments -
Household Appliances -
Information and Communication Products -
Military Equipment
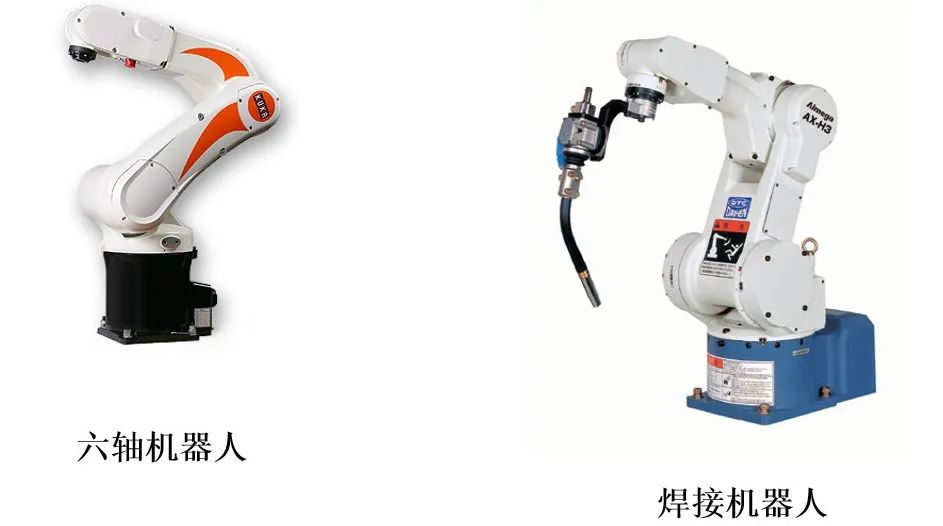


Application of Microcontroller

Long press the image to follow
Discover more exciting content
WeChat ID: Mechanical-knowledge