Skip to content

Source: Wireless Deep Sea
Original Author: Mayfly Cai Cai
What is the maximum speed of Wi-Fi?
Router manufacturers claim that Wi-Fi 6 can achieve speeds of 1800Mbps, 3000Mbps, or even 5400Mbps. How are these figures calculated?
This article will answer your questions.
To calculate the peak speed achievable by Wi-Fi, several technologies must be considered: OFDM, MCS, and MIMO.
OFDM: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing divides the entire system bandwidth into multiple orthogonal subcarriers. The finer the division, the more subcarriers there are, allowing more data to be sent simultaneously, thereby increasing the speed.
Additionally, OFDM technology ultimately packages data into symbols for transmission. The shorter the time taken for each symbol and the smaller the guard interval (GI) between symbols, the higher the speed.
MCS: Modulation and Coding Scheme influences speed mainly through modulation methods and coding rates. The better the wireless environment, the higher the modulation order that can be used, allowing more bits to be carried per unit time. This reduces the redundant bits used for error detection and correction, increasing the coding rate and naturally speeding up the transmission of useful data.
MIMO: This refers to sending multiple data streams simultaneously through multiple antennas. The more spatial streams, the higher the speed. For example, the theoretical speed of 4×4 MIMO is twice that of 2×2 MIMO, providing immediate results.
In summary, the peak speed of a single frequency band Wi-Fi can be calculated using the following formula. Similar to the calculation of 5G peak speed, the above formula can also be analogized to a road system.
The number of spatial streams is analogous to multiple layers of traffic, the number of subcarriers corresponds to multiple lanes on each layer of the road, the modulation order is like the cargo capacity of trucks on the road, the coding rate is akin to adding packaging boxes for the goods, and the OFDM symbol duration and symbol interval represent the travel time of trucks on the road plus the departure interval.
Spatial Streams: With the evolution of protocols, the number of spatial streams supported by Wi-Fi has increased, driving continuous improvements in peak speed.
As shown in the table below, the IEEE 802.11ac standard can support up to 8 streams, but the Wi-Fi Alliance (WFA) deemed this capability too strong during certification, making implementation too costly. Therefore, it was divided into two phases: wave 1 and wave 2.
These two phases also have conservative capabilities and did not ultimately achieve the IEEE design capability. Wave 1 supports 3 streams, while Wave 2 supports 4 streams.
With 802.11ax, it can support up to 8 streams. The Wi-Fi Alliance branded it as Wi-Fi 6 and no longer produced transitional versions. However, the actual number of streams supported by your router depends on the specific implementation by the manufacturer.
Effective Subcarriers: The 802.11 series protocols have increasingly finer divisions of subcarriers, allowing for larger supported channel bandwidths, which has led to a continuous increase in the number of effective subcarriers.
As shown in the table below, 802.11n can support a maximum channel bandwidth of 40M, while 802.11ac can support 160M bandwidth, resulting in a more than fourfold increase in the number of effective subcarriers.
With 802.11ax, it also supports a maximum channel width of 160M, but the subcarrier spacing is only 1/4 of that of previous protocols, thus allowing for a fourfold increase in the maximum number of subcarriers compared to 802.11ac.
Modulation Order: 802.11ac supports a maximum of 256QAM, with a modulation order of 8, meaning each symbol can carry 8 bits of data simultaneously.
802.11ax supports a maximum of 1024QAM, allowing each symbol to carry 10 bits of data simultaneously, a 25% improvement over the previous generation.
MCS and Coding Rate: The protocol defines various combinations of modulation methods and coding rates, known as Modulation Coding Scheme (MCS).
The higher the modulation order, the higher the coding rate, but the worse the anti-interference ability. Therefore, high-order MCS can only be effective when the wireless signal strength is sufficient and interference is minimal.
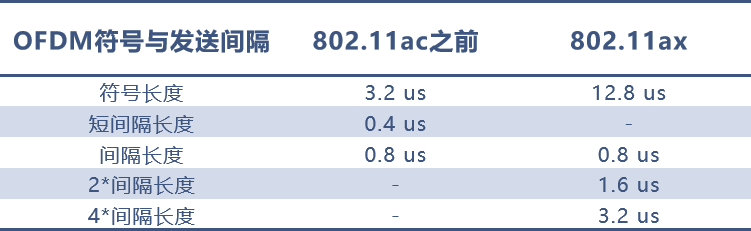
Symbol Length + Symbol Interval: In 802.11ac and earlier, the length of a single symbol is 3.2 microseconds, and the symbol interval is 0.8 microseconds, but it also supports 0.4 microseconds. To calculate peak speed, we naturally use the shorter interval, hence the symbol length + symbol interval for 802.11ac is 3.6 microseconds.
With 802.11ax, the symbol length has become 12.8 microseconds, and the interval length is at least 0.8 microseconds, totaling 13.6 microseconds.
This value, while much higher than previous protocols, may seem like a disadvantage, but 802.11ax excels in other aspects, resulting in a crushing advantage over its predecessors in terms of speed.
By substituting the data from the various tables into the formula, using the highest modulation method and coding rate supported by the protocol, and the minimum symbol interval, without considering spatial streams, the single-stream calculation results are shown in the table below.
The supported peak speed capabilities of different wireless routers vary, mainly reflected in the bandwidth supported by the 2.4G and 5G frequency bands, as well as the number of spatial streams.
The 2.4GHz band typically supports a maximum bandwidth of 40M, while the 5GHz band can support a maximum of 160M bandwidth. By adding the peak speeds supported by these two frequency bands according to different protocol versions and the number of spatial streams, we arrive at the peak speed advertised by the router.
The above image shows the estimated channel bandwidth and stream counts for the 2.4G and 5G frequency bands based on the router’s rated speed, along with verification of the speed calculations.
For example, for AC1200, the AC indicates that it can support the 802.11ac protocol (Wi-Fi 5) at its highest. The 2.4GHz band can only use 802.11n, supporting 2×2 MIMO, with a speed of up to 300Mbps, while the 5GHz band also supports 2×2 MIMO, with a speed of 867Mbps, totaling 1167Mbps, hence advertised as 1200M.
For AX5600, the AX indicates that it can support the 802.11ax protocol (Wi-Fi 6) at its highest. The 2.4GHz band supports 2×2 MIMO, with a speed of up to 573.6Mbps, while the 5GHz band supports 160M channel bandwidth and 4×4 MIMO, with a speed of 4804Mbps, totaling 5377.6Mbps, hence advertised as 5400M.
This content is reproduced and represents only the author’s views.
It does not represent the position of the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences.