Delay Functions
Classification of delay functions:
Relative delay: vTaskDelay
Absolute delay: vTaskDelayUntil
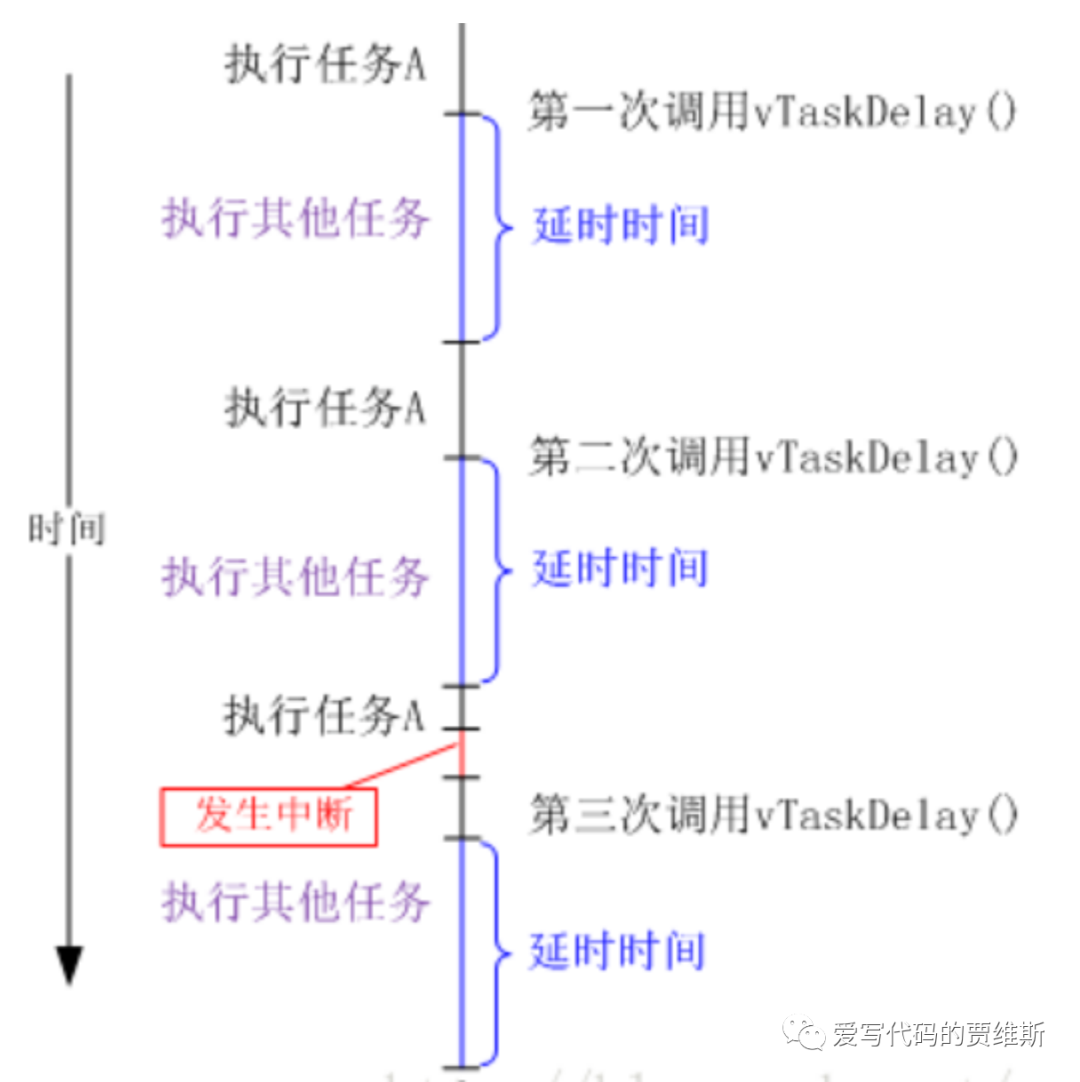
Relative delay
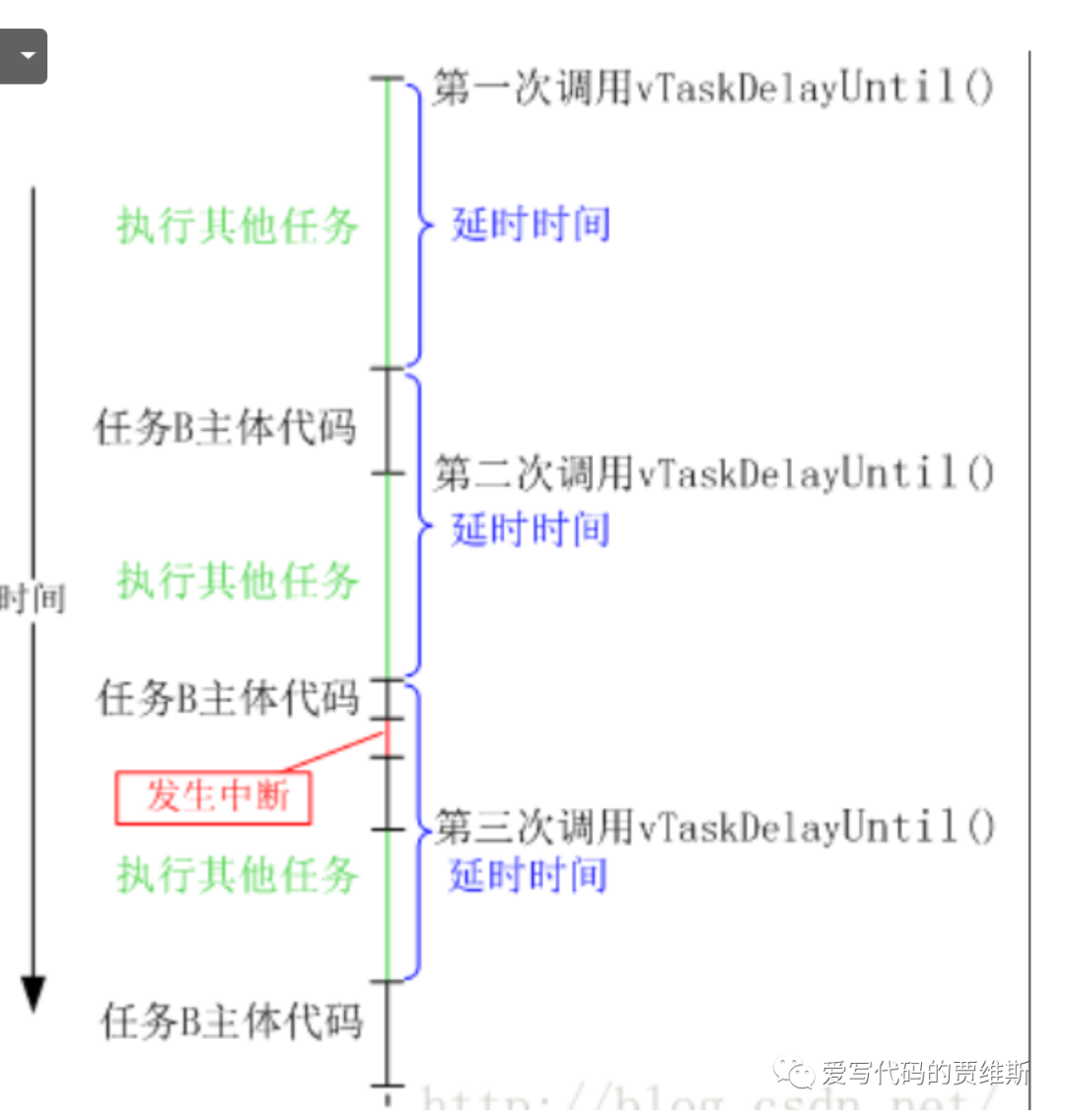
Absolute delay
Relative delay means that each delay starts from the task execution function vTaskDelay() and ends after the specified delay time. Absolute delay means that the task calls the vTaskDelayUntil() function at fixed intervals, in other words, the task executes at a fixed frequency.
Software Timers
Implement timing functions, such as calling a callback function after a certain time, where information can be processed in the callback function.
Advantages: Simple and low cost, can create multiple timers.
Disadvantages: Low precision, easily affected by interrupts.
1. Responsible for the logical judgment of the software timer.
2. Call the timeout callback function of the software timer.
3. Handle the command queue of the software timer.
Software timer related configurations:
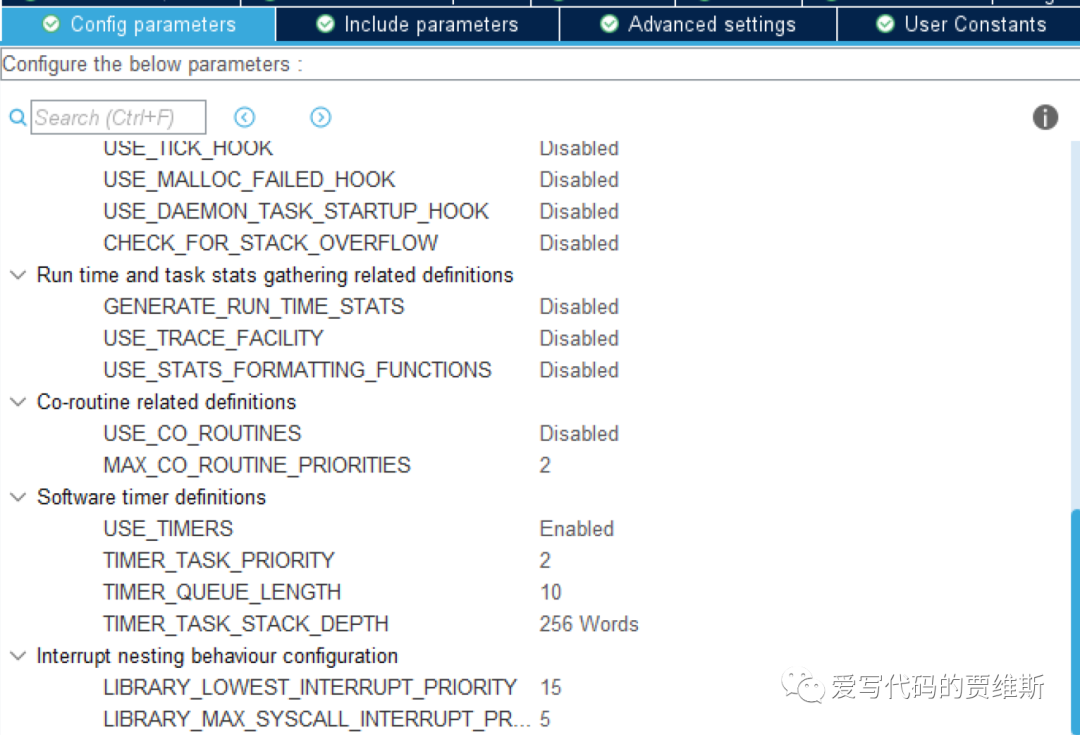
1. configUSE_TIMERS
If you want to use software timers, the macro configUSE_TIMERS must be set to 1. When set to 1, the timer service task will be automatically created when the FreeRTOS scheduler starts.
2. configTIMER_TASK_PRIORITY
The task priority of the timer service task can be set from 0 to (configMAX_PRIORITIES-1). The priority must be set according to the actual application. If the timer service task priority is set high, the timer commands and callback functions will be processed in a timely manner.
3. configTIMER_QUEUE_LENGTH
Use macros to set the length of the timer command queue.
4. configTIMER_TASK_STACK_DEPTH
Use macros to set the stack size of the timer service task.
One-shot Timers and Periodic Timers
One-shot Timer: Calls the callback function once after timeout, manually starts the timer.
Periodic Timer: Calls the callback function multiple times after multiple timeouts.
Timer related API functions:
1. Create a software timer
TimerHandle_t xTimerCreate(const char *const pcTimerName, const TickType_t xTimerPeriod, const UBaseType_t uxAutoReload, void *const pvTimerID, TimerCallbackFunction_t pxCallbackFunction);Parameters:
pcTimerName: Name of the software timer.
xTimerPeriodInTicks: Timeout period, in system clock ticks.
uxAutoReload: Timer mode pdTRUE: periodic timer pdFALSE: one-shot timer.
pvTimerID: Software timer ID, used for multiple timers sharing a single timeout callback function.
pxCallbackFunction: Callback function for the software timer timeout.
Return value:
Success: Timer handle.
Failure: NULL.
2. Start the software timer
BaseType_t xTimerStart(TimerHandle_t xTimer, TickType_t xBlockTime);Parameters: xTimer is the handle waiting to start the software timer.
xTickToWait: Maximum wait time to send a command to the software timer command queue.
Return value:
pdPASS: Start successful.
pdFAIL: Start failed.
3. Stop the software timer
BaseType_t xTimerStop(TimerHandle_t xTimer, TickType_t xBlockTime);Parameters and return values are the same as above;
4. Reset the software timer
BaseType_t xTimerReset(TimerHandle_t xTimer, TickType_t xBlockTime);Parameters and return values are the same as above;
5. Change the timing period of the software timer
BaseType_t xTimerChangePeriod( TimerHandle_t xTimer, TickType_t xNewPeriod, TickType_t xBlockTime);xNewPeriod: New timer timeout period, parameters and return values are the same as above.
Code requirements:
Create two timers:
Timer 1, periodic timer that prints once every second.
Timer 2, one-shot timer that prints once every two seconds after starting.
Cubemx configuration:
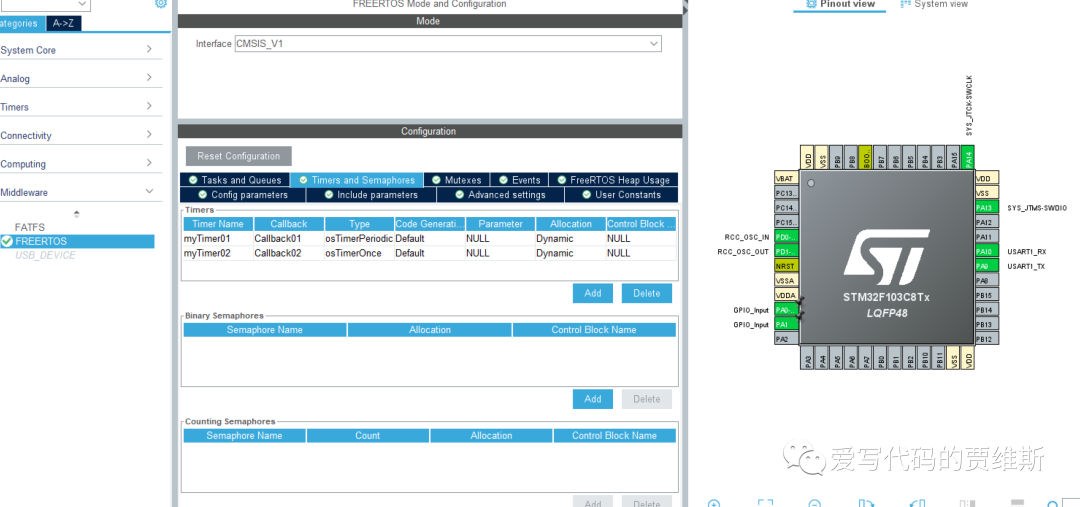
void StartTaskLed1(void const * argument){ /* USER CODE BEGIN StartTaskLed1 */ //osTimerStart(myTimer01Handle,1000); xTimerChangePeriod(myTimer01Handle,pdMS_TO_TICKS(100),0);// Change software timer time osTimerStart(myTimer02Handle,2000); /* Infinite loop */ for(;;) { osDelay(1); } /* USER CODE END StartTaskLed1 */}Task function
void Callback01(void const * argument){ /* USER CODE BEGIN Callback01 */printf("hello\r\n"); /* USER CODE END Callback01 */} /* Callback02 function */void Callback02(void const * argument){ /* USER CODE BEGIN Callback02 */printf("world!\r\n"); /* USER CODE END Callback02 */}Callback functions
Display effect