China Electrical Engineering Society Activity Area
CES Conference




Reading Tip: This article has about 1600 words
Currently, the most mature power supply method for wireless sensor networks is battery power. However, this method requires frequent battery replacements, which leads to reduced power supply reliability. Single-wire power transfer can balance transmission distance and efficiency, while also being flexible and omnidirectional, thus addressing the battery power issue in wireless sensor networks. Researchers Li Yang, Li Yao, Wang Rui, Zhai Yujie, Shi Shaobo, and Hu Taocheng from Tianjin University of Technology’s Key Laboratory of New Electrical Power Technology published related research results in the 4th issue of the Journal of Electrical Engineering in 2022. The research shows that compared to systems with capacitive spheres, the physical quantities of systems without capacitive spheres are all lower, which better complies with safety standards limiting time-varying electric and magnetic fields.
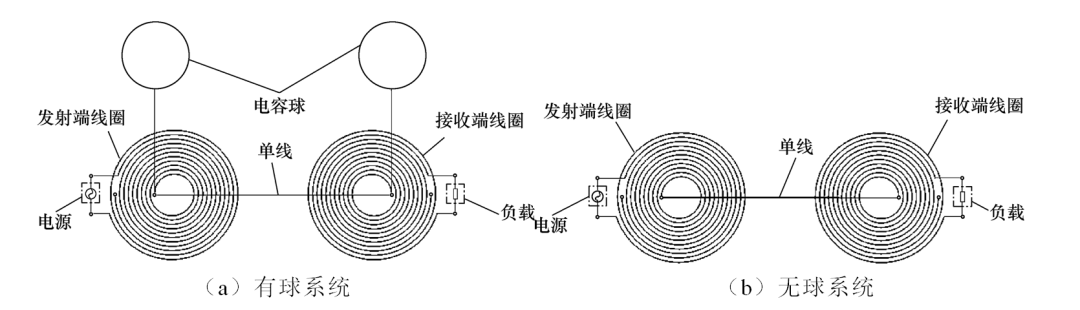
Figure 1 Two Types of Single-Wire Power Transfer System Structures
The research on the electromagnetic safety of single-wire power transfer systems can help understand the working process and transmission mechanism of the single-wire power transfer system; on the other hand, it provides a basis for reducing the electromagnetic radiation produced by the single-wire power transfer system. Studying the electromagnetic safety of single-wire power transfer systems requires considering the biological effects in the electromagnetic environment. A small amount of electromagnetic radiation can cause skin heating and nerve pain, while a large amount can lead to nerve disorders, heart failure, burns, or even death. Currently, the electromagnetic radiation standards adopted in China are GB 8702 2014 “Limits for Electromagnetic Environment Control,” while representative international electromagnetic field radiation standards include IEEE C95.1 and ICNIRP guidelines.
Researchers from Tianjin University of Technology’s Key Laboratory of New Electrical Power Technology first established models of single-wire power transfer systems with and without capacitive spheres, as well as human body models. They then performed simulation analysis of the electromagnetic safety of both system models, primarily comparing the spatial electromagnetic field distribution, spatial electromagnetic field intensity, internal electric field intensity, and internal current density of both systems. Finally, experimental methods were used to validate the simulation results.
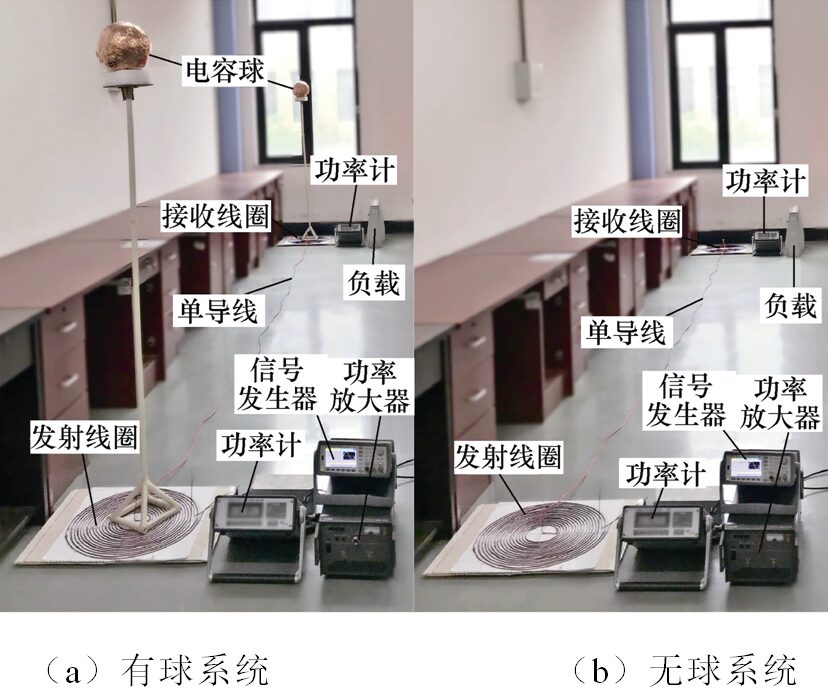
Figure 2 Experimental System
This article is adapted from the 4th issue of the Journal of Electrical Engineering in 2022, titled “Electromagnetic Safety Analysis of Wireless Sensor Network Power Transfer System,” authored by Li Yang, Li Yao, et al.
-
First Look | Table of Contents and Abstracts of the 4th Issue of the Journal of Electrical Engineering 2022 -
Call for Papers for the 17th Academic Annual Meeting of the China Electrical Engineering Society (First Round)
-
Good News! The “Academic Annual Meeting of the China Electrical Engineering Society” has been included in the China Association for Science and Technology’s “Important Academic Conference Guide (2022)”
-
Call for Papers for the 2022 International Conference on Wireless Power Transfer Technology (ICWPT2022)
-
Professor Xu Dianguo from Harbin Institute of Technology: Outlook on the Future Development Direction of Power Electronics and Power Transmission Disciplines under the Dual Carbon Goals
-
Professor Liu Jinjun from Xi’an Jiaotong University: What Challenges Might Power Electronics Face in the Next 70 Years?
-
How to Mitigate the Impact of Structural Electromagnetic Forces on the Coupling Mechanism of Wireless Power Transfer Systems? Researchers from Hebei University of Technology Propose Solutions
-
The Research Team from Tianjin University of Technology Publishes a Review of Coupling Mechanisms in Magnetic Field Coupling Wireless Power Transfer Systems
-
The Research Team from Shanghai University of Electric Power Achieves New Progress in the Research on the Reduction of Small Signal Models in Wireless Power Transfer Systems
-
Researchers from Chongqing University Publish a Review of Research on Electric Field Coupling Wireless Power Transfer Technology



Official WeChat of the Society
Journal of Electrical Engineering
CES Electrical



Official Bilibili of the Society
CES TEMS
Today’s Toutiao Account



Society’s Science Popularization WeChat
Sina Weibo
Douyin Account
Contact Us
Journal of Electrical Engineering: 010-63256949/6981
Email: [email protected]
Electrical Technology: 010-63256943
Email: [email protected]
Editorial Office: 010-63256994; Subscription: 010-63256817
Advertising Cooperation: 010-63256867/6838