With the development of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) have become an ideal choice for connecting a large number of devices. Among these LPWAN technologies, LoRa and LoRaWAN are the two most widely used. Although they are closely related, LoRa and LoRaWAN differ technically, and understanding the differences between them is crucial for designing and deploying IoT solutions.
1. LoRa (Long Range)
LoRa is a physical layer (PHY layer) technology focused on providing low-power, long-range wireless communication. The LoRa technology was developed by Semtech and uses Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) modulation, enabling effective data transmission in low signal-to-noise ratio environments. The main features of LoRa include:
·Long-range communication: LoRa supports communication distances of 2-5 kilometers in urban environments, while in open areas, the maximum communication distance can reach 15 kilometers or even further.
·Low power consumption: LoRa devices can operate in low-power mode, extending battery life, and can typically work for years without needing a battery replacement.
·High interference resistance: Due to the use of spread spectrum modulation, LoRa can maintain a high quality of data transmission in noisy wireless environments.
·Low data rate: The typical data rate for LoRa ranges from 0.3 kbps to 27 kbps, making it suitable for low-bandwidth applications such as sensor data collection and telemetry.
2. LoRaWAN (LoRa Wide Area Network)
LoRaWAN is a network protocol based on the LoRa physical layer, defining how LoRa devices communicate over a wide area network. LoRaWAN primarily handles high-level communication protocols, including communication rules between devices, network architecture, device authentication, encryption mechanisms, and more. LoRaWAN technology is designed to meet the needs of large-scale IoT applications, featuring the following characteristics:
·Network architecture: LoRaWAN employs a star network architecture, where devices communicate directly with gateways, which are responsible for forwarding data to the network server. This architecture supports millions of devices connecting to the same network simultaneously.
·End-to-end encryption: LoRaWAN provides end-to-end encryption mechanisms to ensure data security. Each device generates a unique encryption key upon joining the network to protect the confidentiality and integrity of its communication data.
·Device management: LoRaWAN supports remote management of devices, Over The Air (OTA) configuration updates, and status monitoring, effectively managing large-scale device deployments.
·Multiple communication modes: LoRaWAN supports three main communication modes: Class A (most suitable for low-power applications), Class B (for applications requiring periodic communication), and Class C (for applications with high real-time communication requirements).
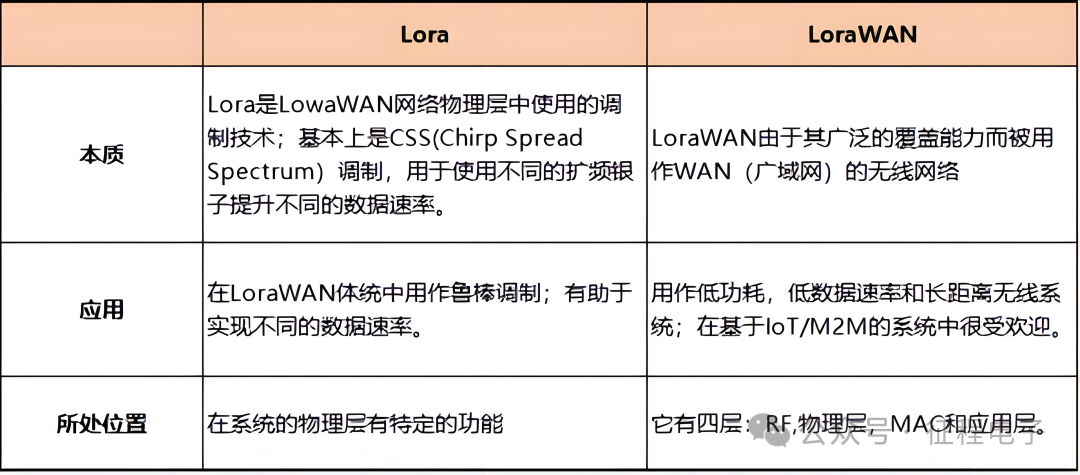
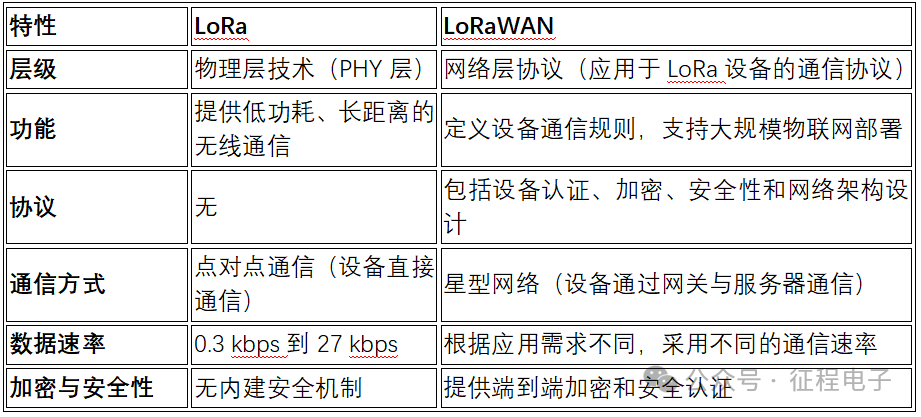
3. Main Differences Between LoRa and LoRaWAN
4. Relationship Between LoRa and LoRaWAN
LoRa and LoRaWAN are often used together, but they address different technical issues. LoRa provides the physical layer communication capability, supporting long-range, low-power wireless data transmission, while LoRaWAN builds on LoRa to provide protocol support for large-scale IoT networks, including network management, data encryption, and device authentication. In simple terms, LoRaWAN is an extension and specification of LoRa technology at the application layer.
5. Application Scenarios
LoRa and LoRaWAN are widely used in various IoT scenarios, especially where low power consumption, long range, and large-scale device support are required. Common applications include:
·Smart Agriculture: Collecting data on soil moisture, climate changes, etc., through sensors and transmitting it to a central server for analysis and management via LoRaWAN.
·Smart Cities: Used in smart lighting, waste management, public transport monitoring, etc., LoRaWAN can ensure that a large number of devices connect simultaneously and transmit data effectively.
·Energy Monitoring: Used for remote monitoring of electricity, water, and other infrastructure, LoRa technology can provide stable communication over vast areas.
·Environmental Monitoring: Used for air quality monitoring, water level monitoring, etc., enabling remote data transmission and real-time monitoring through LoRaWAN.

6. Conclusion
LoRa and LoRaWAN, as core components of Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology, provide long-range wireless communication capabilities and network protocols that support large-scale device access, respectively. LoRa is a physical layer technology focused on the fundamental performance of wireless communication, while LoRaWAN is the protocol layer based on LoRa, offering advanced features such as device management, network architecture, and data encryption. In practical applications, LoRa and LoRaWAN are typically used together to achieve remote communication and large-scale deployment of IoT devices.
