To upgrade a laptop motherboard, it is essential to know what components on the motherboard can be upgraded.
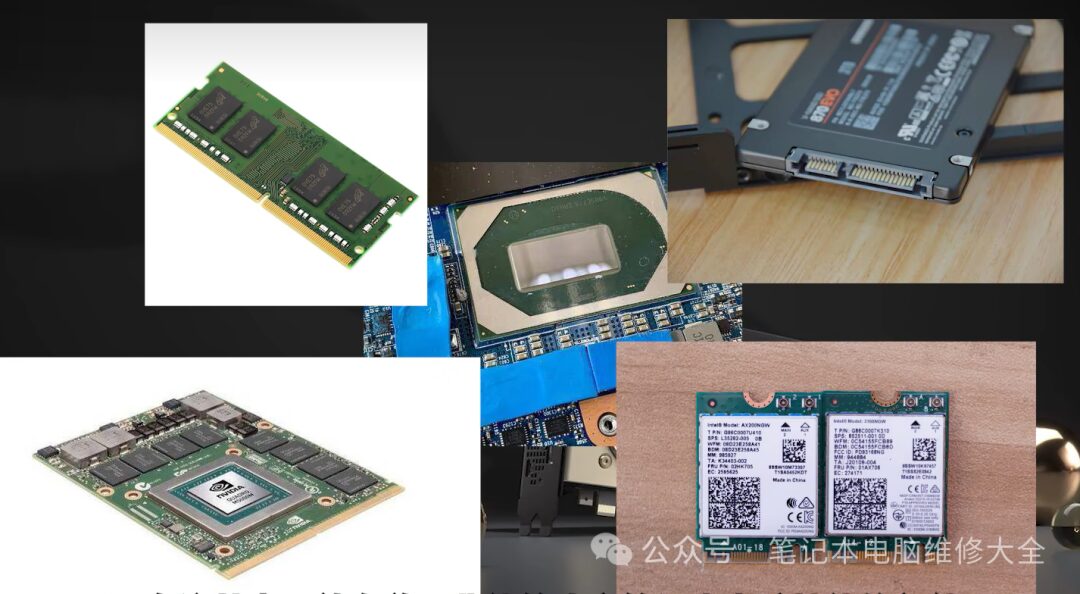

If you open your laptop or search online for images of laptop motherboards, you will find that the motherboard is composed of numerous components, some of which determine the performance of the laptop. Today, let us review the components on a laptop motherboard that can be upgraded. Friends who need to upgrade their laptops, please like, save, and follow.
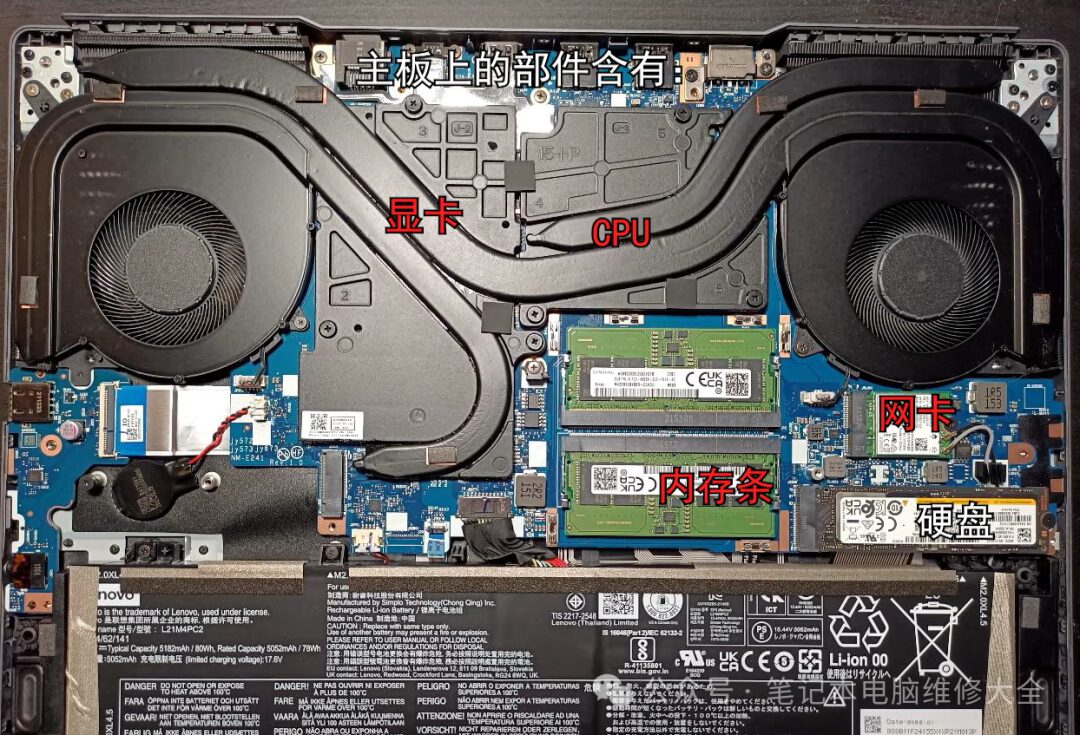
In this introduction, upgrading refers to expanding the scale of components, updating their architecture, or enhancing their performance, which can change the role of the components to a certain extent. Based on the above description, we can identify five components that can be considered upgradeable. Their introductions are as follows:
-
Hard Drive. Upgrade Frequency: 5 Stars
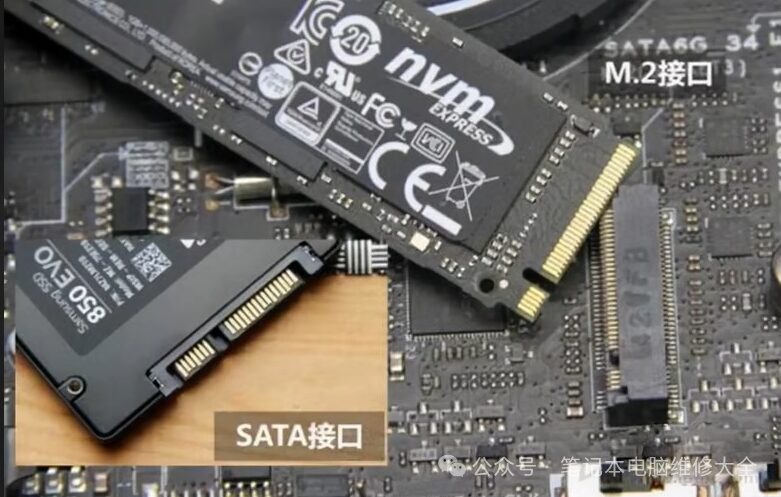
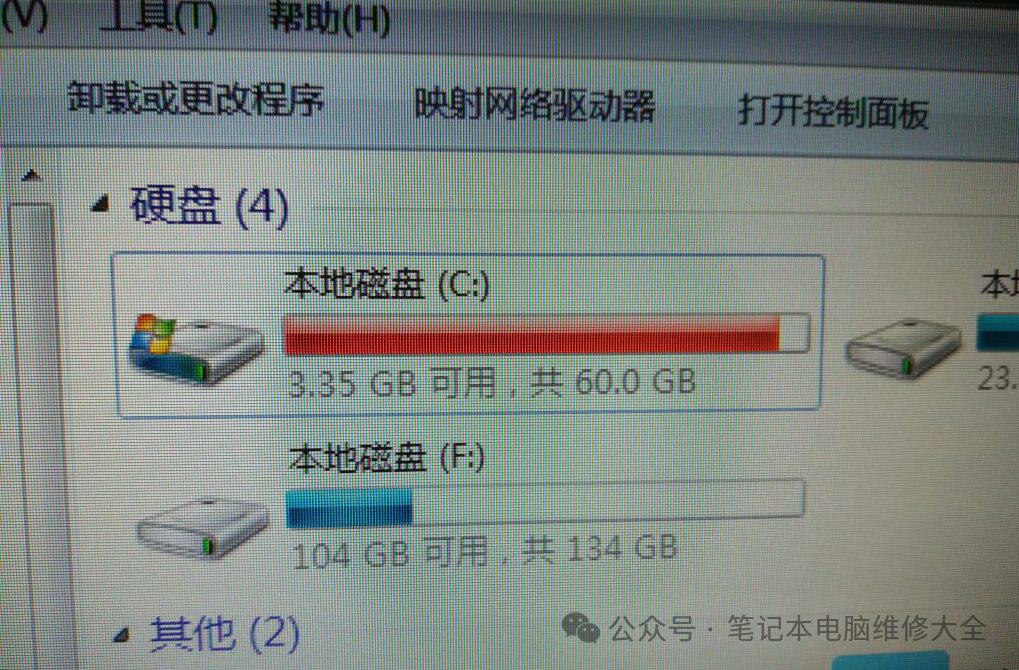
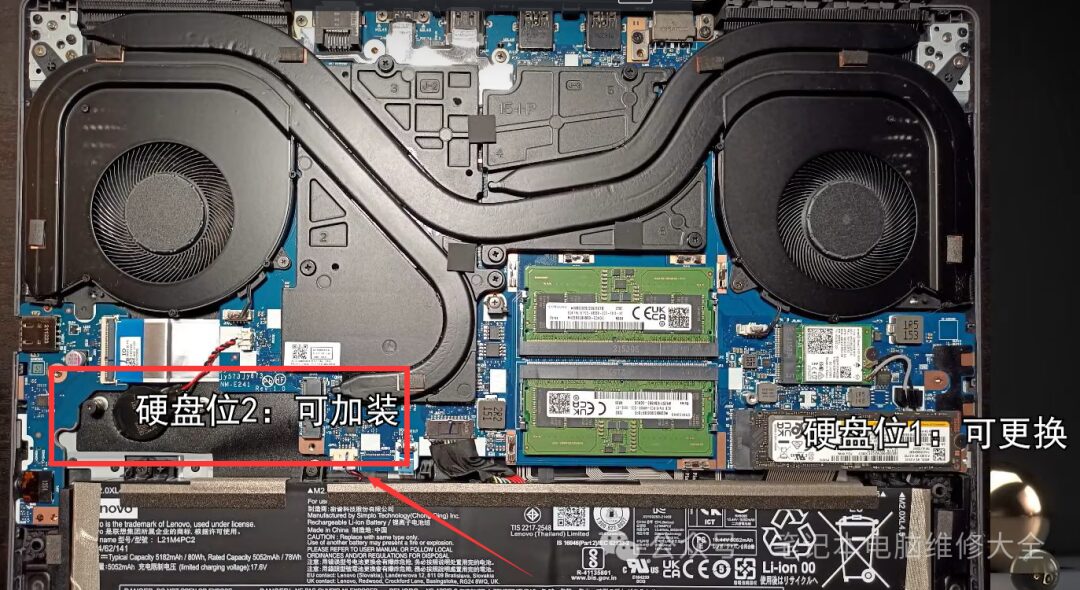
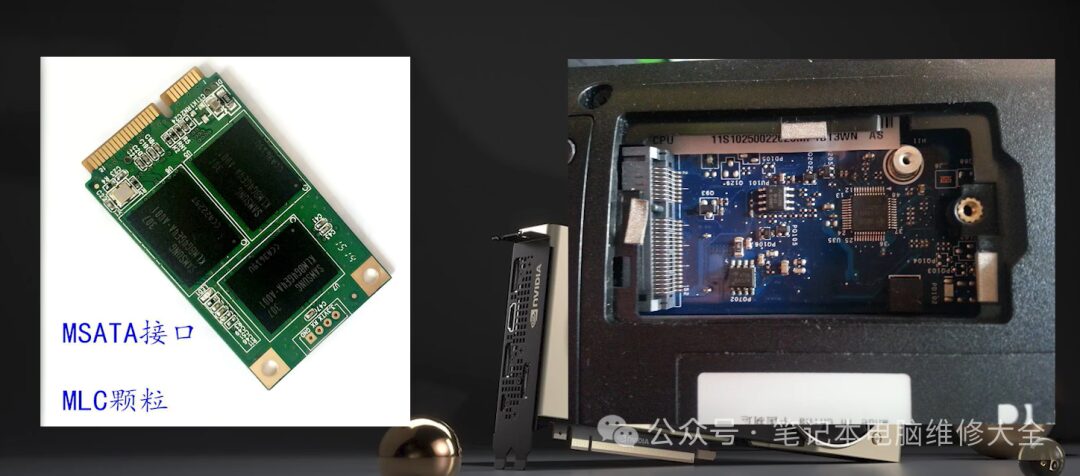
During the lifespan of a laptop, many users face issues with insufficient storage. At this point, upgrading the hard drive can solve the problem. Most modern laptops come with hard drives that users can replace, including NVME and SATA interface hard drives, as well as older NGFF or mSATA interface hard drives. Only a few laptops have hard drives soldered directly onto the motherboard. These hard drives cannot be expanded by users; instead, one must choose an external hard drive or seek help from repair personnel. It is best to choose a slightly larger capacity when purchasing.

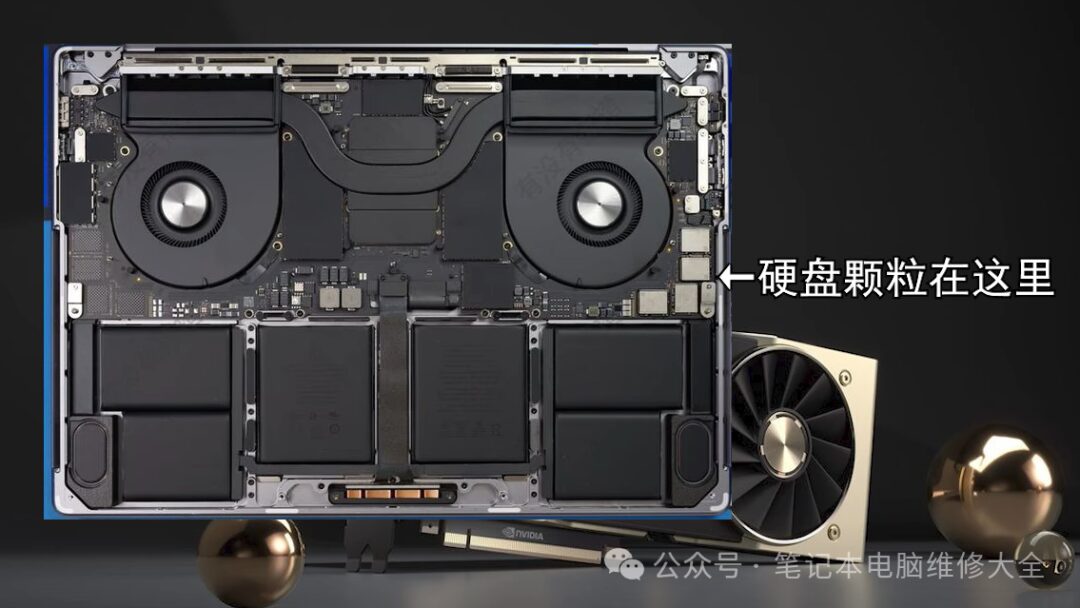

2. Memory Stick. Upgrade Frequency: 4 Stars
Many users also face issues with insufficient memory during the usage of their laptops. In this case, adding or replacing memory sticks can solve the problem. Most modern gaming laptops, versatile laptops, and a few lightweight laptops support memory stick replacements. Currently, widely used DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 memory sticks correspond only to their respective slots and are not compatible with each other.
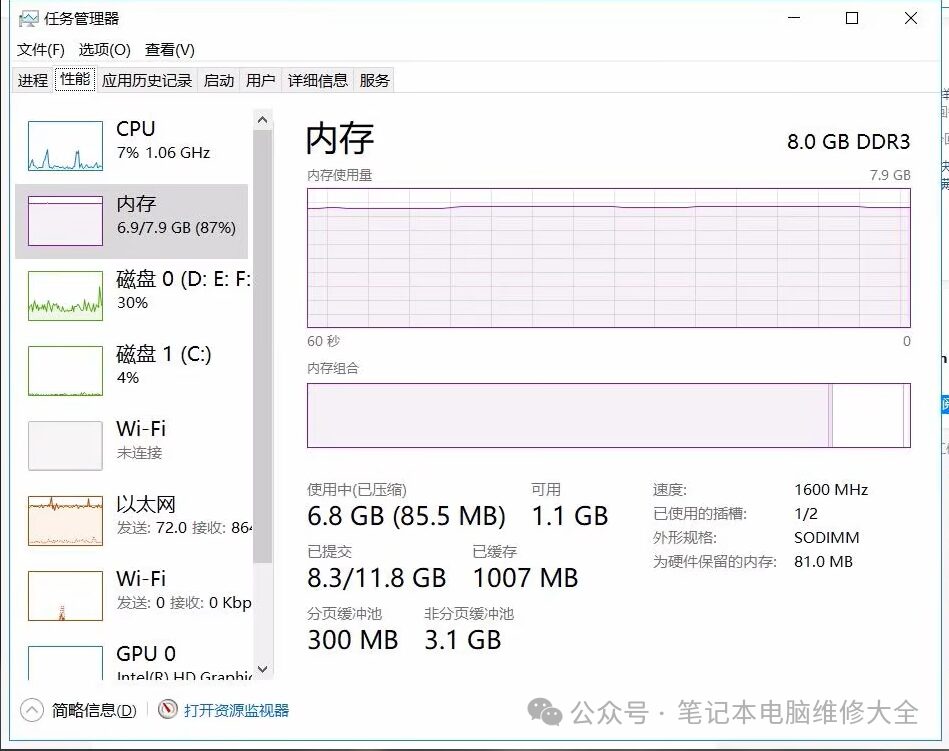

Many lightweight laptops have memory chips soldered onto the motherboard. In such cases, users cannot expand the memory themselves and must seek help from repair personnel. It is advisable to select a slightly larger capacity when purchasing such laptops.
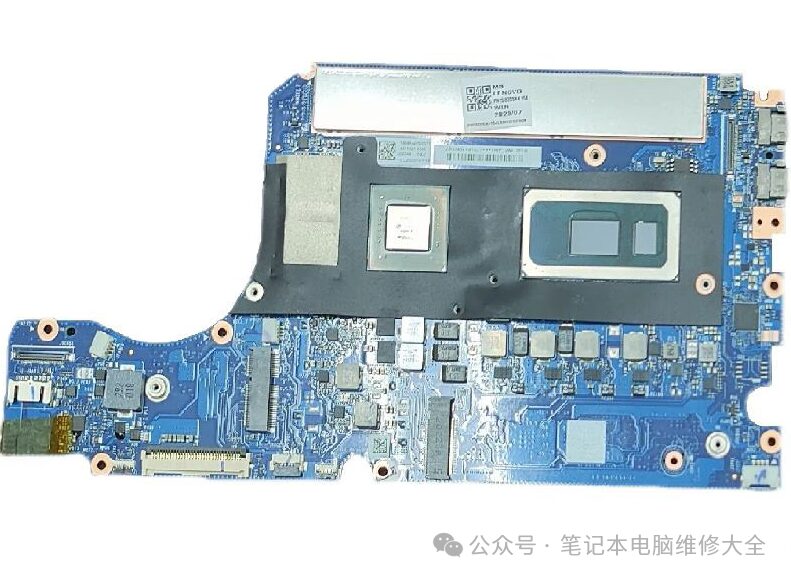

3. Wireless Network Card. Upgrade Frequency: 2 Stars
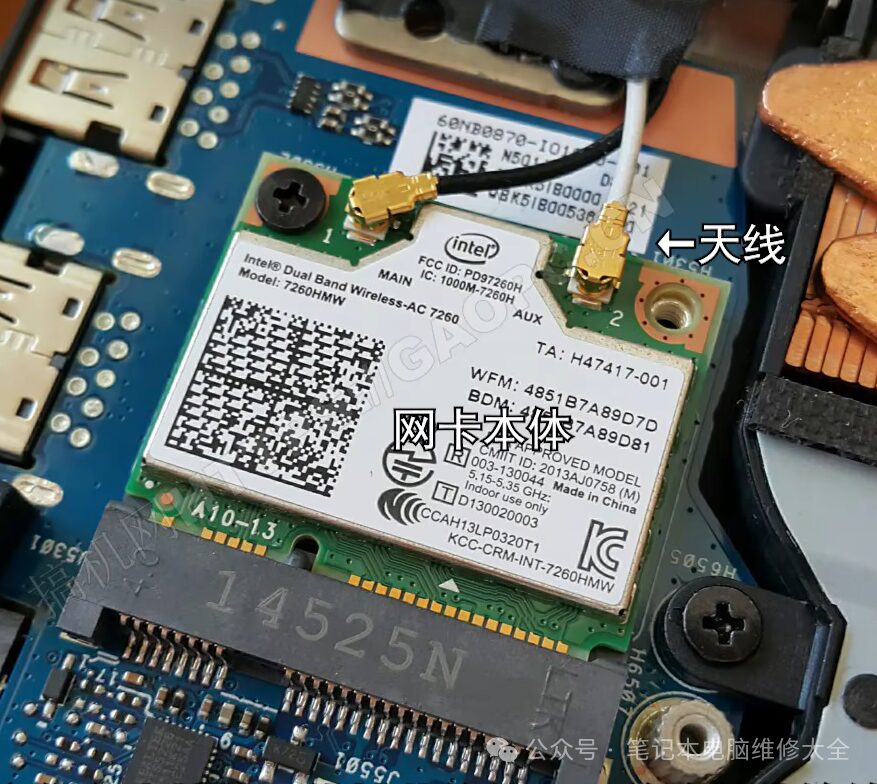

Wireless network cards, also known as wireless modules, are responsible for receiving signals captured by antennas and transmitting them to processors and other components. WiFi wireless network cards are one type of these. However, for most users, the speed of the network card is not a significant issue. The primary concern is whether it can function correctly. Therefore, even though most laptops come with user-replaceable network cards, most users will not replace them unless there are disconnection issues or major design flaws with the network card.
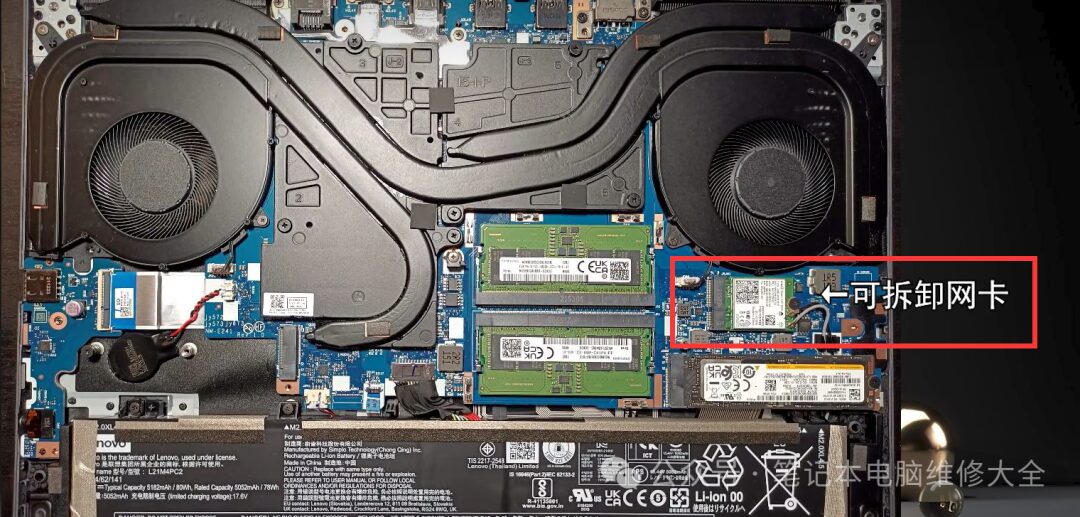
There are also a few network cards that are directly integrated into the motherboard. These network cards tend to be of better quality, but if they malfunction, they can only be repaired.

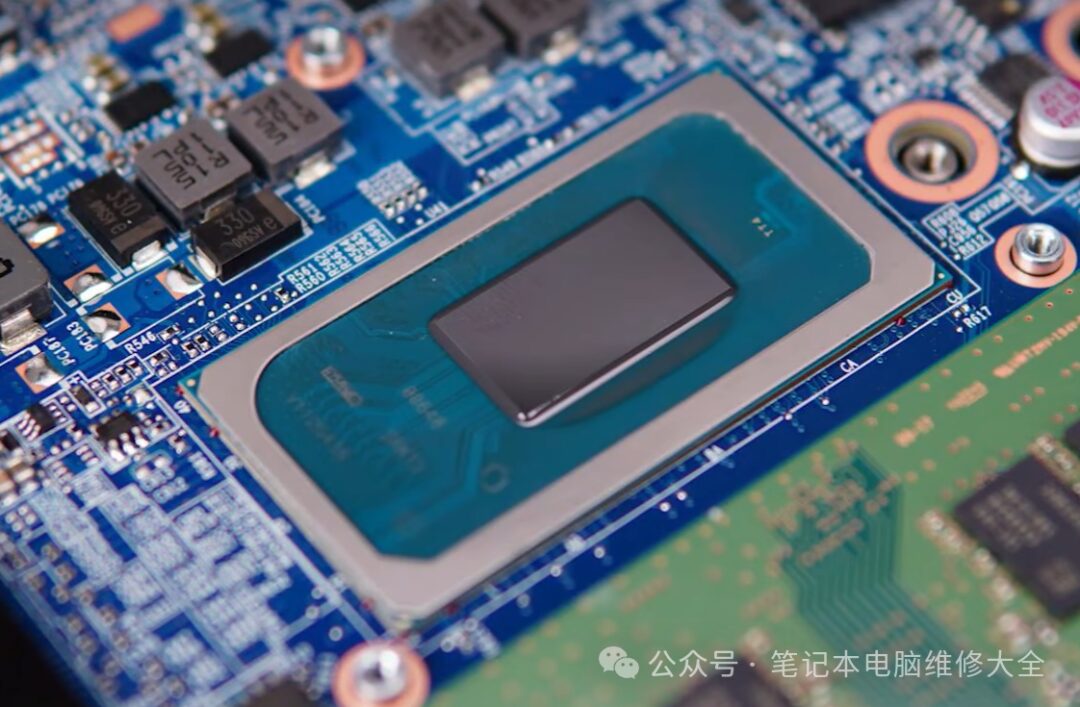
4. CPU. Upgrade Frequency: 2 Stars
The central processing unit is the core component of the computer and largely determines its performance. Some users may upgrade the CPU when its performance is limited. In fact, upgrading the CPU in laptops is not uncommon. In the past, it was common for laptop motherboards to have CPU sockets, and this trend peaked during the third and fourth generations of Core processors.
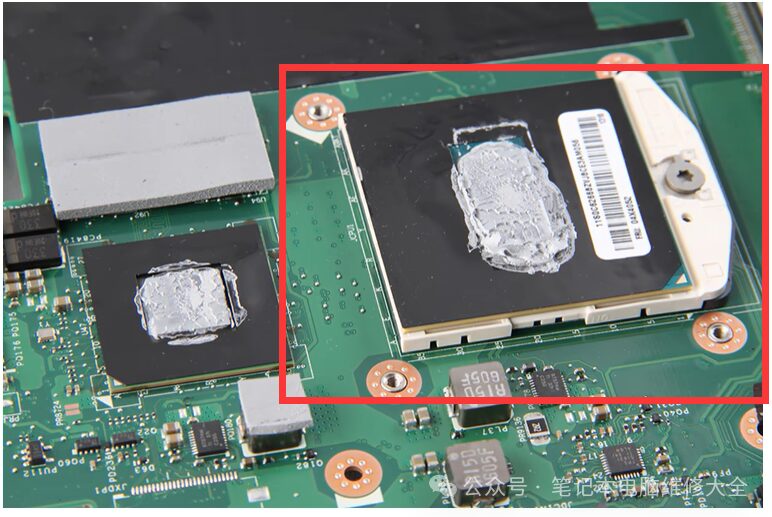

After the fifth generation of Core processors, manufacturers eliminated CPU sockets in laptops due to the need for thinner designs. Currently, only niche systems support user-replaceable CPUs, and these laptops tend to be heavier; the rest have CPUs soldered onto the motherboard in BGA packaging, which does not allow users to replace them and must be done by repair personnel.

5. Graphics Card. Upgrade Frequency: 1 Star.
The graphics card is responsible for the computer’s graphics processing tasks and plays a significant role in gaming, modeling, and other graphical data processing fields. Users used to replace graphics cards in laptops, but only a few older models had MXM slots for graphics cards, which used MXM interfaces for transmission through PCI channels. This trend continued into the NVIDIA 10 series era. Although MXM graphics cards still exist today, they are only found in a few niche systems and have undergone deep customization by manufacturers, making them incompatible with other brands’ systems.
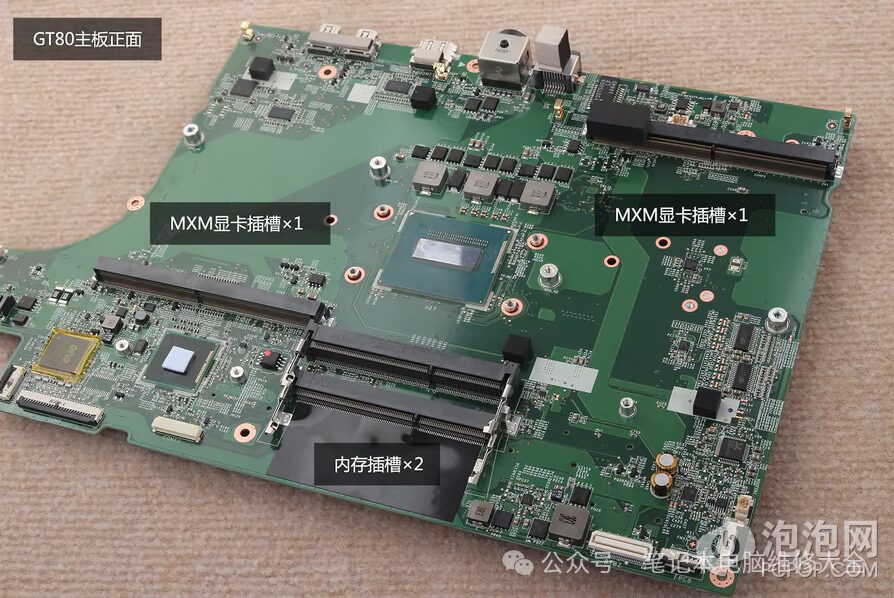

Currently, most graphics cards on laptops are soldered onto the motherboard, and different models have different pin configurations, making it challenging for repair personnel to upgrade them.
That concludes today’s introduction to the upgradeable components on laptop motherboards. If you have any additions or questions, please leave a message in the background, and I will respond to each one.
Finally: Most Important:Disassembly carries risks; repairs require caution. For any repair issues, feel free to consult me, the price is reasonable.