📌 Problem Description
Write a program to output the first n terms of the Fibonacci sequence (starting from 1, in the form of 1, 1, 2, 3, 5…).
Requirements:1. Support input of any positive integer n2. Optimize time complexity to O(n)Example:
Input: n=5 → Output: 1 1 2 3 5 Input: n=1 → Output: 1 Difficulty: ⭐ (suitable for learners mastering loops and recursion)
💡 Basic Implementation (Iterative Method)
#include <stdio.h>
void print_fibonacci(int n) { if (n < 1) return; int a = 1, b = 1; printf("The first %d terms of the Fibonacci sequence:", n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", a); int next = a + b; a = b; b = next; }}
int main() { int n; printf("Input n:"); scanf("%d", &n); print_fibonacci(n); return 0;}Output Example:
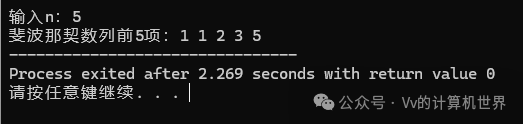
🔥 Recursive Implementation (Understanding the Concept, Not Recommended for Practical Use)
#include <stdio.h>
int fib(int n) { if (n == 1 || n == 2) return 1; return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);}
int main() { int n; printf("Please enter the number of Fibonacci sequence terms to calculate: "); scanf("%d", &n);
if (n <= 0) { printf("The number of terms must be a positive integer.\n"); return 1; }
printf("The first %d terms of the Fibonacci sequence are: ", n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { printf("%d ", fib(i)); } printf("\n");
return 0;} // Note: Recursive method has a time complexity of O(2ⁿ), suitable only for teaching demonstration🔥 Optimized Implementation (Advanced: Dynamic Programming)
#include <stdio.h>
void print_fib_opt(int n) { if (n < 1) return; int dp[n]; dp[0] = dp[1] = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", dp[i]); } printf("\n");}
int main() { int n; printf("Please enter the number of Fibonacci sequence terms to calculate: "); if (scanf("%d", &n) != 1) { printf("Invalid input, please enter an integer.\n"); return 1; } if (n <= 0) { printf("The number of terms must be a positive integer.\n"); return 1; } printf("The first %d terms of the Fibonacci sequence are: ", n); print_fib_opt(n); return 0;} Advantages:
-
Time complexity O(n), space complexity O(n)
-
Can quickly query the value of any term
🤔 Common Problem Analysis
| Problem | Error Code | Correct Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Boundary case n=0 not handled | Direct loop causes crash | Add<span>if (n < 1) return</span> |
| Incorrect number of output terms | <span>i <= n</span> → Outputs one extra term |
<span>i < n</span> |
| Value overflow | Did not handle large n causing int overflow | Change to<span>long long</span> type |
🎯 Extension Challenge
Try to implement the following features (choose any one):
-
Output the nth term (without using an array, space complexity O(1))
-
Support large number output (e.g., n=100, using string handling)
-
Graphically print the sequence (spiral arrangement, triangle, etc.)
🚀 Next Issue Preview No. 18 Pascal’s Triangle: Can You Print a Symmetrical Triangle Using a Two-Dimensional Array?
📢 Interaction Time
- What other fascinating properties of the Fibonacci sequence do you know? Feel free to leave a comment!
-
Vote:
🚀 If you find it useful, feel free to share it with friends learning C language!
Article Author:Vv Computer Graduate Examination World (focusing on computer graduate examination guidance for8 years)
Original Statement: Please contact for authorization to reprint, infringement will be pursued.