CMake is an open-source, cross-platform suite of tools for building, testing, and packaging software. CMake controls the software compilation process using simple platform and compiler-independent configuration files (CMakeLists.txt) and generates native build files and workspaces that can be used in your chosen build environment. The CMake suite was created by Kitware in response to the demand for a robust cross-platform build environment for open-source projects like ITK and VTK.
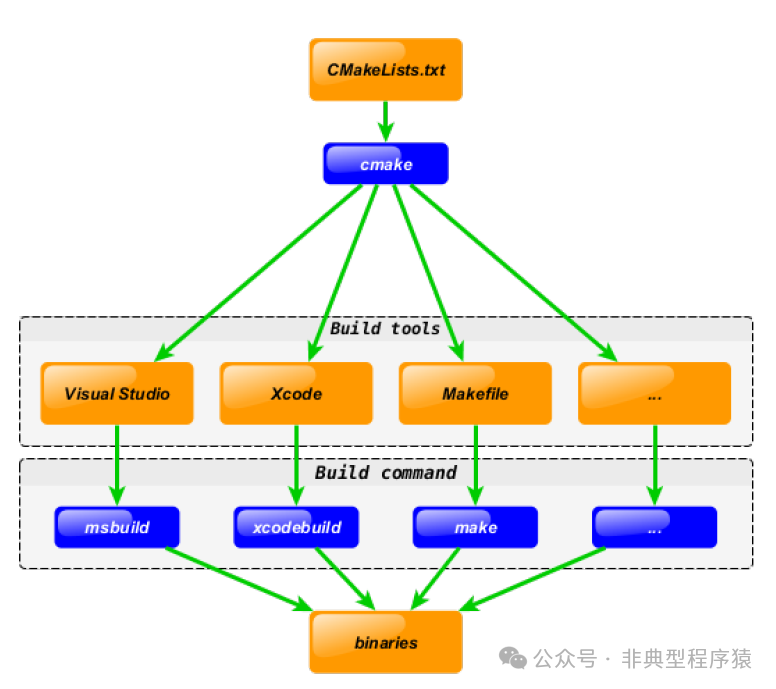
CMake is a meta-build system. It can generate real native build tool files from abstract text configurations. Such code typically resides in CMakeLists.txt files.
1. Installing CMake
This section introduces the installation process using Ubuntu 18.04 Server as an example.
Download the specified version of CMake from https://cmake.org/files/. Here we download https://cmake.org/files/v3.22/cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
1. Download cmake-3.22.0
wget https://cmake.org/files/v3.22/cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
--2021-12-06 01:05:45-- https://cmake.org/files/v3.22/cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
Resolving cmake.org (cmake.org)... 66.194.253.25
Connecting to cmake.org (cmake.org)|66.194.253.25|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 45044059 (43M) [application/x-gzip]
Saving to: ‘cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz’
cmake-3.22.0-linux- 100%[===================>] 42.96M 24.0KB/s in 18m 51s
2021-12-06 01:24:37 (38.9 KB/s) - ‘cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz’ saved [45044059/45044059]
2. Extract the compressed package
tar zxvf cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
List the directory tree of the cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64 folder. If the tree command is not supported, install it first.
Install tree:
sudo apt install tree
tree -L 2 cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64
The directory tree of cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64 is as follows:
cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64
├── bin
│ ├── ccmake
│ ├── cmake
│ ├── cmake-gui
│ ├── cpack
│ └── ctest
├── doc
│ └── cmake
├── man
│ ├── man1
│ └── man7
└── share
├── aclocal
├── applications
├── bash-completion
├── cmake-3.22
├── emacs
├── icons
├── mime
└── vim
3. Create a symbolic link
Move cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64 to the /opt/cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64 folder (the file path can be specified, generally chosen under /opt or /usr).
sudo mv cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64 /opt/cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64
Create symbolic links for the files under cmake bin.
sudo ln -sf /opt/cmake-3.22.0-linux-x86_64/bin/* /usr/bin/
4. Confirm the installation result
cmake --version
The output is as follows, indicating that the installed version of cmake is 3.22.0.
cmake version 3.22.0
CMake suite maintained and supported by Kitware (kitware.com/cmake).
2. CMake Hello World
Preparation before using CMake.
mkdir test
cd test
touch main.cpp
touch CMakeLists.txt
main.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"hello world!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
# Minimum required version of cmake
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
# Project name
project(HELLOWORLD)
# Include the original program, i.e., copy the source program from the given directory to the variable DIR_SRC
aux_source_directory(. DIR_SRC)
# Generate the program
add_executable(helloworld ${DIR_SRC})
Create a build directory to generate the output files after CMake compilation.
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../
Clearly, an error occurred.
CMake Deprecation Warning at CMakeLists.txt:2 (cmake_minimum_required):
Compatibility with CMake < 2.8.12 will be removed from a future version of
CMake.
Update the VERSION argument <min> value or use a ...<max> suffix to tell
CMake that the project does not need compatibility with older versions.
CMake Error: CMake was unable to find a build program corresponding to "Unix Makefiles". CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM is not set. You probably need to select a different build tool.
CMake Error: CMAKE_C_COMPILER not set, after EnableLanguage
CMake Error: CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER not set, after EnableLanguage
-- Configuring incomplete, errors occurred!
See also "/home/snake/test/build/CMakeFiles/CMakeOutput.log".
Compatibility with CMake < 2.8.12 will be removed in future versions, so the CMakeLists.txt needs to be changed:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
CMake cannot find a build program corresponding to “Unix Makefiles”. CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM is not set. You may need to select a different build tool. You need to install the build tool, here we choose to install make.
sudo apt-get -y install make
make -v
The output of make -v is as follows:
GNU Make 4.1
Built for x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Copyright (C) 1988-2014 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
CMAKE_C_COMPILER and CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER are not set, installing g++ will solve this.
sudo apt install g++
It is clear that CMake still needs to be paired with make and g++ to compile.
Re-enter the build directory:
cmake ..
Now CMake is working properly.
-- The C compiler identification is GNU 7.5.0
-- The CXX compiler identification is GNU 7.5.0
-- Detecting C compiler ABI info
-- Detecting C compiler ABI info - done
-- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc - skipped
-- Detecting C compile features
-- Detecting C compile features - done
-- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info
-- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info - done
-- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ - skipped
-- Detecting CXX compile features
-- Detecting CXX compile features - done
-- Configuring done
-- Generating done
-- Build files have been written to: /home/snake/test/build
List the files in the build directory again, the Makefile is familiar, so calling the make command again will generate the executable bin file. CMake originally only generated the Makefile and did not directly generate the final executable binary file!
CMakeCache.txt CMakeFiles cmake_install.cmake Makefile
Execute the make command in the build directory.
make
The output is as follows:
[ 50%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/helloworld.dir/main.cpp.o
[100%] Linking CXX executable helloworld
[100%] Built target helloworld
The helloworld bin executable file has been generated.
Run the helloworld bin program in the build directory.
./helloworld
The output is as follows:
hello world!
3. Common CMake Commands
Specifically, CMake commands are divided into three types: script commands, project commands, and CTest commands.
3.1 project
Sets the name of the project and stores it in the variable PROJECT_NAME. When called from the top-level CMakeLists.txt, it also stores the project name in the variable CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME.
project(<PROJECT-NAME> [<language-name>...])
project(<PROJECT-NAME>
[VERSION <major>[.<minor>[.<patch>[.<tweak>]]]]
[DESCRIPTION <project-description-string>]
[HOMEPAGE_URL <url-string>]
[LANGUAGES <language-name>...])
3.2 cmake_minimum_required
Sets the minimum required CMake version for a project and also updates policy settings.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION <min>[...<policy_max>] [FATAL_ERROR])
<min> and the optional <policy_max> are CMake formatted versions: major.minor[.patch[.tweak]]
If the running CMake version is lower than the required version <min>, it will stop processing the project and report an error. The optional <policy_max> must be at least the <min> version if specified and affects policy settings as described in the policy settings. If the running version of CMake is older than 3.12, the additional … dots will be treated as version component separators, causing the … part to be ignored, retaining the pre-3.12 policy behavior based on <min>.
This command sets the value of the CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED_VERSION variable to <min>.
The FATAL_ERROR option is ignored by CMake versions 2.6 and above.
Policy Settings
The cmake_minimum_required(VERSION) command implicitly calls the cmake_policy(VERSION) command to specify that the current project code is written for the given range of CMake versions. All known running versions of CMake that are known to be <min> (or <max> if specified) or earlier will be set to use NEW behavior. All policies introduced in later versions will be unset. This effectively requests preferred behavior as a given CMake version and informs new CMake versions to warn about their new policies.
When a <min> version above 2.4 is specified, it is the version implicitly called by this command.
cmake_policy(VERSION <min>[...<max>])
3.3 aux_source_directory
Find all source files in a directory. Collect the names of all source files in the specified directory and store the list in the provided <variable> variable. This command is used for projects with explicitly instantiated templates. Template instantiation files can be stored in a Templates subdirectory and automatically collected using this command to avoid manually listing all instantiations.
This command can avoid writing source file lists for libraries or executable targets. While this may seem feasible, CMake cannot generate a build system that knows when new source files are added. The generated build system typically knows when it needs to re-run CMake because the CMakeLists.txt file is modified to add a new source file. When source code is simply added to the directory without modifying that file, CMake must be manually re-run to generate a build system that includes the new files.
aux_source_directory(<dir> <variable>)
3.4 add_executable
Add an executable target named <name> built from the source files listed in the command call. <name> corresponds to the logical target name and must be globally unique within the project. The actual filename of the built executable is constructed according to local platform conventions (e.g., <name>.exe or just <name>).
add_executable(<name> [WIN32] [MACOSX_BUNDLE]
[EXCLUDE_FROM_ALL]
[source1] [source2 ...])
3.5 set
Set normal variables, cache variables, or environment variables to a given value.
Set normal variables
Set the given <variable> variable within the current function or directory scope.
set(<variable> <value>... [PARENT_SCOPE])
Set cache variables
Set the given cache <variable> variable (cache entry). Since cache entries are intended to provide user-settable values, they do not overwrite existing cache entries by default. Use the FORCE option to overwrite existing entries.
set(<variable> <value>... CACHE <type> <docstring> [FORCE])
Set environment variables
Set the environment variable to a given value. Subsequent calls to $ENV{<variable>} will return this new value.
set(ENV{<variable>} [<value>])
3.6 add_subdirectory
Add a subdirectory to the build. source_dir specifies the directory where the source CMakeLists.txt and code files are located. If it is a relative path, it will be calculated based on the current directory (this is typical usage), but it can also be an absolute path. binary_dir specifies the directory where output files will be stored. If it is a relative path, it will be evaluated based on the current output directory, but it can also be an absolute path. If binary_dir is not specified, the value of source_dir will be used before expanding any relative paths (typical usage). CMake will immediately process the CMakeLists.txt file in the specified source directory and then continue processing the current input file.
If the EXCLUDE_FROM_ALL parameter is provided, then targets in the subdirectory will not be included in the parent directory’s ALL target by default and will be excluded from IDE project files. Users must explicitly build targets in the subdirectory. This is applicable for subdirectories that contain a separate part of the project that is useful but not essential, such as a set of examples.
add_subdirectory(source_dir [binary_dir] [EXCLUDE_FROM_ALL])
3.7 find_library
This command is used to find libraries. A cache entry or a normal variable (if NO_CACHE is specified), <VAR> variable is used to store the result of this command. If the library is found, the result is stored in the variable, and unless the variable is cleared, it will not search again. If nothing is found, the result will be <VAR>-NOTFOUND.
find_library (<VAR> name1 [path1 path2 ...])
find_library (
<VAR>
name | NAMES name1 [name2 ...] [NAMES_PER_DIR]
[HINTS [path | ENV var]... ]
[PATHS [path | ENV var]... ]
[PATH_SUFFIXES suffix1 [suffix2 ...]]
[DOC "cache documentation string"]
[NO_CACHE]
[REQUIRED]
[NO_DEFAULT_PATH]
[NO_PACKAGE_ROOT_PATH]
[NO_CMAKE_PATH]
[NO_CMAKE_ENVIRONMENT_PATH]
[NO_SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PATH]
[NO_CMAKE_SYSTEM_PATH]
[CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_BOTH |
ONLY_CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH |
NO_CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH]
)
3.8 file
This command is specifically for file and path operations that require access to the file system.
Reading
file(READ <filename> <out-var> [...])
file(STRINGS <filename> <out-var> [...])
file(<HASH> <filename> <out-var>)
file(TIMESTAMP <filename> <out-var> [...])
file(GET_RUNTIME_DEPENDENCIES [...])
Writing
file({WRITE | APPEND} <filename> <content>...)
file({TOUCH | TOUCH_NOCREATE} [<file>...])
file(GENERATE OUTPUT <output-file> [...])
file(CONFIGURE OUTPUT <output-file> CONTENT <content> [...])
Filesystem
file({GLOB | GLOB_RECURSE} <out-var> [...] [<globbing-expr>...])
file(MAKE_DIRECTORY [<dir>...])
file({REMOVE | REMOVE_RECURSE } [<files>...])
file(RENAME <oldname> <newname> [...])
file(COPY_FILE <oldname> <newname> [...])
file({COPY | INSTALL} <file>... DESTINATION <dir> [...])
file(SIZE <filename> <out-var>)
file(READ_SYMLINK <linkname> <out-var>)
file(CREATE_LINK <original> <linkname> [...])
file(CHMOD <files>... <directories>... PERMISSIONS <permissions>... [...])
file(CHMOD_RECURSE <files>... <directories>... PERMISSIONS <permissions>... [...])
Path Conversion
file(REAL_PATH <path> <out-var> [BASE_DIRECTORY <dir>] [EXPAND_TILDE])
file(RELATIVE_PATH <out-var> <directory> <file>)
file({TO_CMAKE_PATH | TO_NATIVE_PATH} <path> <out-var>)
Transfer
file(DOWNLOAD <url> [<file>] [...])
file(UPLOAD <file> <url> [...])
Locking
file(LOCK <path> [...])
Archiving
file(ARCHIVE_CREATE OUTPUT <archive> PATHS <paths>... [...])
file(ARCHIVE_EXTRACT INPUT <archive> [...])
3.9 add_definitions
Add -D define flags when compiling source files.
add_definitions(-DFOO -DBAR ...)
3.10 add_library
Add a library to the project using the specified source files.
add_library(<name> [STATIC | SHARED | MODULE]
[EXCLUDE_FROM_ALL]
[<source>...])
add_library(<name> OBJECT [<source>...])
add_library(<name> INTERFACE)
add_library(<name> <type> IMPORTED [GLOBAL])
add_library(<name> ALIAS <target>)
3.11 target_include_directories
Specify the include directories to be used when compiling the given target. <target> must be created by commands like add_executable() or add_library() and cannot be an ALIAS target.
target_include_directories(<target> [SYSTEM] [AFTER|BEFORE]
<INTERFACE|PUBLIC|PRIVATE> [items1...]
[<INTERFACE|PUBLIC|PRIVATE> [items2...] ...])
3.12 target_link_libraries
Specify the libraries or flags to be used when linking the given target and/or its dependencies. The usage requirements from the linked library targets will be propagated. The usage requirements of target dependencies will affect the compilation of their own sources.
target_link_libraries(<target> ... <item>... ...)
3.13 set_target_properties
Targets can have properties that affect how they are built. Set the properties of the target. The syntax of this command is to list all the targets you want to change, then provide the values you want to set next.
set_target_properties(target1 target2 ...
PROPERTIES prop1 value1
prop2 value2 ...)
3.14 include_directories
Add include directories to the build.
include_directories([AFTER|BEFORE] [SYSTEM] dir1 [dir2 ...])
3.15 message
Log messages.
General messages
message([<mode>] "message text" ...)
Reporting checks
message(<checkState> "message text" ...)
4. Practical CMake: Porting Live555
Write a CMakeLists.txt for porting Live555 to the Android platform.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
set(LIVE555_LIB_NAME Live555)
file(GLOB BasicUsageEnvironmentFiles ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/BasicUsageEnvironment/*.cpp)
file(GLOB groupsockFiles ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/groupsock/*.cpp ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/groupsock/*.c)
file(GLOB liveMediaFiles ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/liveMedia/*.cpp ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/liveMedia/*.c)
file(GLOB UsageEnvironmentFiles ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/UsageEnvironment/*.cpp)
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/BasicUsageEnvironment/include/)
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/groupsock/include/)
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/liveMedia/include/)
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/UsageEnvironment/include/)
add_definitions(-D LOCALE_NOT_USED)
# Android version higher than 24 can use getifaddrs, freeifaddrs
add_definitions(-D NO_GETIFADDRS)
# bind() error (port number: 8554): Address already in use
add_definitions(-D ALLOW_SERVER_PORT_REUSE)
set(OPENSSL_LIBS_DIR ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/../../../../libs)
message(STATUS "OPENSSL_LIBS_DIR = ${OPENSSL_LIBS_DIR}.")
add_library(crypto STATIC IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(crypto
PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION ${OPENSSL_LIBS_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libcrypto.a)
add_library(ssl STATIC IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(ssl
PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION ${OPENSSL_LIBS_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libssl.a)
include_directories(${OPENSSL_LIBS_DIR}/include/)
find_library(z-lib z)
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
${LIVE555_LIB_NAME}
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
${BasicUsageEnvironmentFiles}
${groupsockFiles}
${UsageEnvironmentFiles}
${liveMediaFiles})
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
${LIVE555_LIB_NAME}
# Links the target library to the third library
# included in the NDK.
ssl
crypto
${z-lib})
After compilation, an error occurred: invalid conversion from ‘int*’ to ‘socklen_t*’
Modify line 123 of groupsock/include/NetCommon.h
#define SOCKLEN_T int changed to #define SOCKLEN_T socklen_t
References:
- https://cmake.org/cmake/help/latest/manual/cmake-commands.7.html
Non-typical Programmer–☆ Linking the programmer community, the wheels of fate begin to turn ☆–Welcome to followIf you find it useful, remember tolike and share with more people