
This is my 324th column article.
The integration of large AI models with hardware is in full swing, but it seems to be facing resistance on the B2C consumer side.
According to The Information, former Apple design chief Jony Ive and OpenAI CEO Sam Altman have teamed up to design an AI-driven personal device and are seeking at least $1 billion in funding. However, the B2C smart hardware based on the latest AI large model released in recent weeks has been met with ridicule and criticism, such as the Humane Pin and Rabbit R1. Early buyers believe that the usability of these devices is significantly inferior to that of smartphones.

Despite the obstacles faced by large model hardware in the B2C sector, the combination of large models and edge computing has made breakthrough progress in the B2B sector, advancing the evolution of Intelligent IoT 2.0 and making solid strides towards the integration of “communication, perception, intelligence, and value.”
As more and more enterprises begin to integrate sensors, communication gateways, controllers, and actuators, a “communication, perception, intelligence, and value integration” is formed.
This article will explore the latest developments in the combination of large models and edge computing, and how “communication, perception, intelligence, and value integration” can create greater value.
Three Major Trends of Edge Intelligence: Cloud Training Delegation, NPU Acceleration, Tiny AI Empowerment
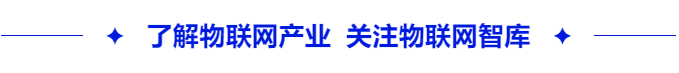
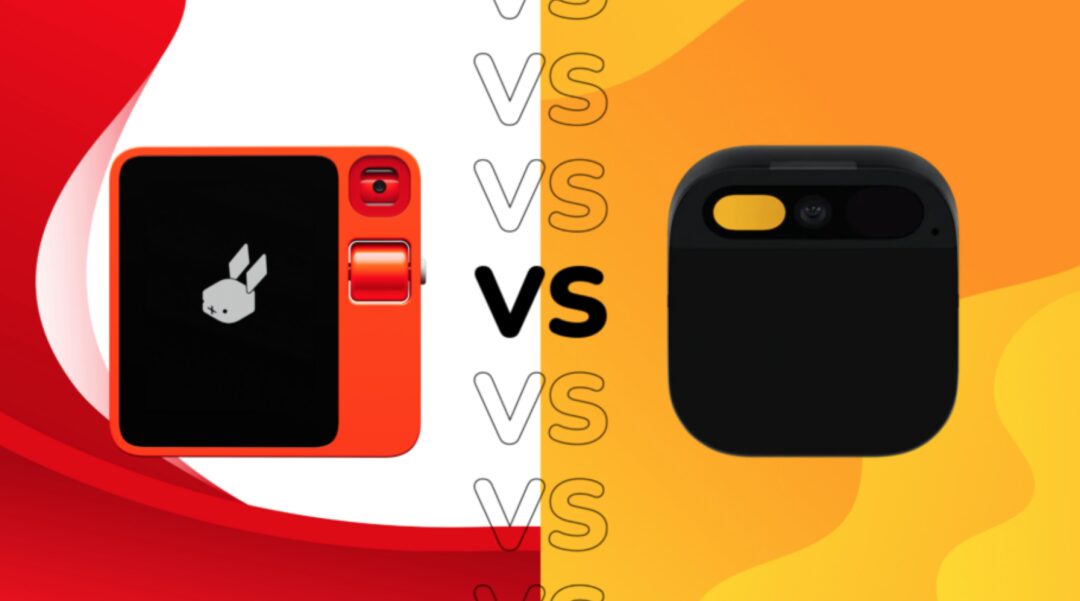
Edge computing refers to deploying intelligent computing resources near the source of data generation or consumption. Depending on the computing power and deployment location, edges can be divided into three types: infrastructure edge (thick edge), device edge (thin edge), and terminal edge (micro edge).
-
Infrastructure Edge (Thick Edge): Typically located within data centers, equipped with high-performance Central Processing Units (CPUs) or Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), specifically designed to handle compute-intensive tasks such as data storage and analysis. Typical thick edge devices include cellular wireless base stations, regional data centers, and certain specific central machine rooms.
-
Device Edge (Thin Edge): Includes smart controllers, network devices, and computers that are responsible for aggregating data from sensors and other data-generating devices. Common thin edge devices include IoT gateways, switches, routers, and local servers.
-
Terminal Edge (Micro Edge): Refers to intelligent sensors and devices that directly generate data.
Edge intelligence refers to deploying AI models on edge devices, enabling them to perform AI inference and decision-making without a continuous connection to the cloud.
Currently, edge intelligence is showing three major development trends: cloud training delegation to thick edge, NPU acceleration for thin and micro edges, and Tiny AI empowerment for micro edges.
1. Cloud Burden Delegation, AI Model Training Migrates to Thick Edge
With the integration of high-performance CPUs and GPUs, AI model training is shifting from centralized cloud to edge servers or micro data centers. This not only reduces dependence on cloud infrastructure and costs but also enhances data privacy protection, improving the responsiveness of AI applications on edge devices.
This trend helps achieve on-site processing and analysis of data, reducing data transmission over the network, thereby lowering latency and security risks, and enhancing the real-time and reliability of AI applications.
For example, the PRO AI workstation jointly launched by MAINGEAR and Phison, as well as Aetina’s AIP-FR68 edge AI training platform, embody this trend.

2. NPU Chip Empowerment, Micro and Thin Edge AI Inference Acceleration
Integrating dedicated Neural Processing Units (NPUs) in micro and thin edge devices can significantly enhance their AI inference capabilities while saving power and optimizing thermal management, achieving efficient multitasking. This allows AI to be widely deployed in applications sensitive to power consumption and latency, such as wearable devices and sensor nodes.
The addition of NPUs equips edge devices with powerful AI computing capabilities, enabling them to complete complex inference tasks locally, greatly reducing dependence on the cloud and improving the real-time and privacy of data processing.
NXP’s new MCX N series Microcontroller (MCU) and ARM’s Cortex A55+Ethos U65 NPU setup demonstrate the performance improvements brought by NPU integration. NXP’s MCU machine learning inference speed is 42 times faster than that of a standalone CPU core; ARM offloads 70% of AI inference from the CPU to the NPU, improving inference performance by 11 times.

3. Tiny AI Empowerment, Traditional Devices Become Micro Edge AI
Tiny Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (Tiny AI/ML) further brings AI capabilities to resource-constrained micro edge devices. By integrating small AI/ML models into everyday items and tools, they can autonomously execute decision-making functions without cloud connectivity, enhancing data privacy and security while granting traditional devices intelligent capabilities.
The emergence of Tiny AI greatly expands the application scenarios and scope of AI, allowing traditional “dumb” devices to become intelligent, possessing certain perception, learning, and decision-making abilities, laying the foundation for the arrival of the Intelligent IoT 2.0 era.
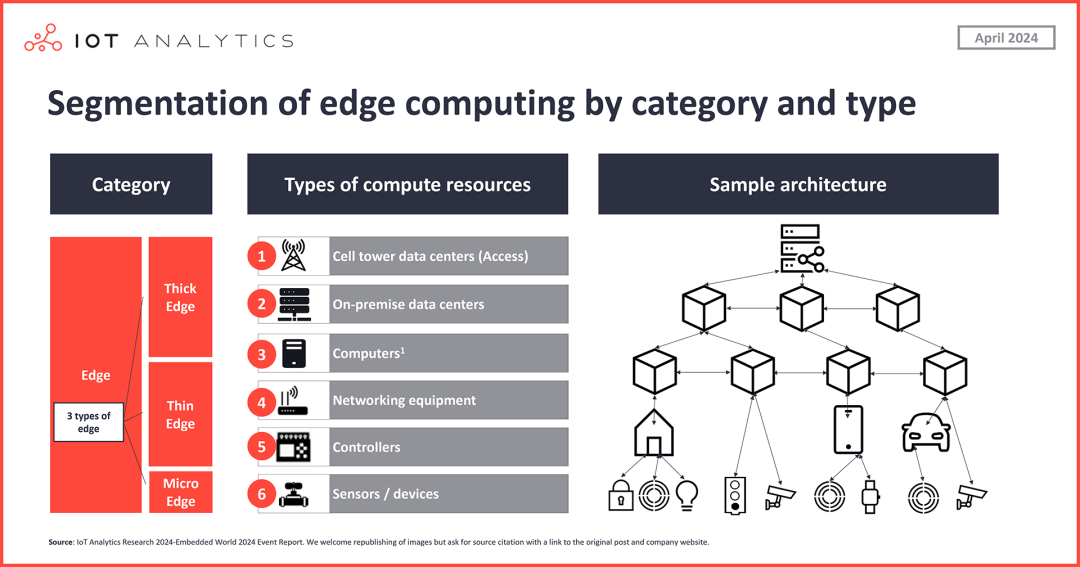
For example, MY VOICE AI’s NANOVOICE voice verification solution, SensiML’s smart drill anomaly detection model, and Nordic Semiconductor’s Thingy:53 prototype device are all innovative applications of micro AI/ML in micro edge devices. For instance, Thingy:53 uses embedded micro machine learning models to sense device vibrations, and the system can cut off the power supply to devices or machines when anomalies are detected.
Cellular IoT Modules Enter a New Stage, AI Computing Power Becomes a Key Driving Force
As artificial intelligence and cellular IoT continue to merge, integrating AI chipsets directly into IoT devices has become an emerging trend. This marks the rise of intelligent, autonomous IoT systems capable of making real-time decisions locally.
This trend is expected to bring revolutionary changes to fields such as smart cities and industrial manufacturing, enabling real-time data processing, reducing latency, and improving efficiency through smaller device sizes.
In this wave, smart modules and AI cellular IoT modules have become important engines driving market growth. These modules are equipped with embedded computing resources that can perform complex data analysis and even AI inference tasks directly on IoT devices. It is expected that by 2027, the shipment of these advanced modules will continue to climb at a compound annual growth rate of 76%.
In fact, the concept of “computing power modules” often mentioned in the industry overlaps significantly with smart modules and AI-enabled cellular IoT modules, representing the latest development direction of cellular IoT technology. Market research agency Counterpoint has also found that in 2023, about 12% of the products shipped by module manufacturers have AI capabilities at the software and hardware levels. These modules are becoming increasingly popular in high-end markets such as automotive, routers/CPE, and PCs, helping to cope with the growing data load in these fields.
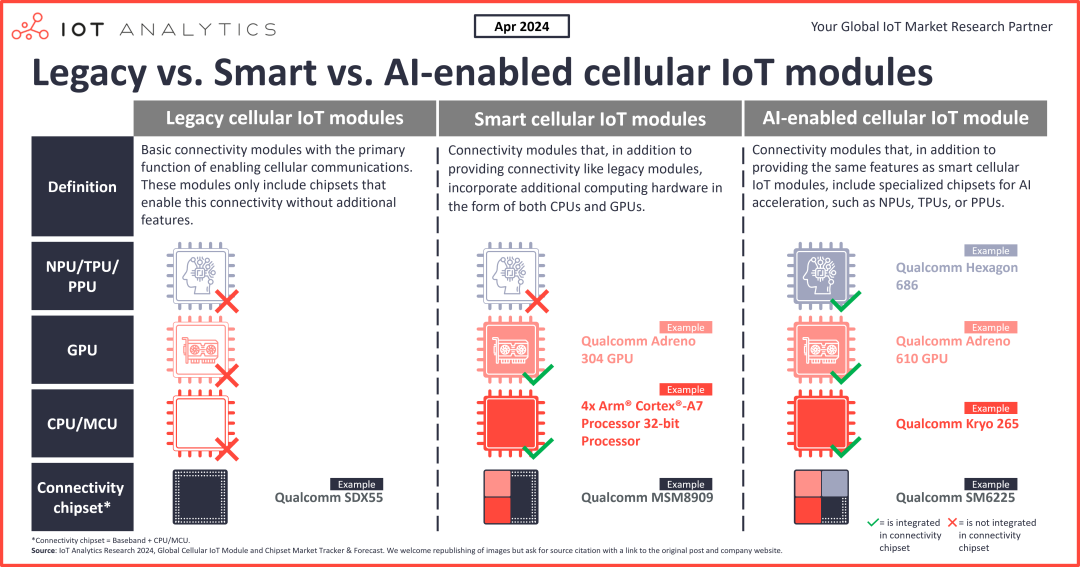
Overall, the development history of cellular IoT modules can be divided into three overlapping stages: traditional modules, smart modules, and AI-enabled modules.
-
Traditional IoT Modules serve as basic connectivity modules, primarily functioning to enable cellular communication, containing only chipsets that support communication without additional features.
-
Smart IoT Modules not only provide connectivity but also integrate additional computing hardware, such as Central Processing Units (CPUs) and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs).
-
AI-Enabled IoT Modules further integrate dedicated AI acceleration chipsets, such as Neural Processing Units (NPUs), Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), or Parallel Processing Units (PPUs), based on smart modules.
Compared to traditional and smart modules, AI-enabled cellular IoT modules have been introduced relatively recently. However, they are expected to completely change the landscape of various industries. By integrating AI directly into IoT modules, AI inference can be executed in real-time on the edge side, enabling quick, autonomous local decision-making. This not only reduces data transmission on cellular networks, saving bandwidth and costs but also meets the immediate decision-making needs of time-sensitive applications.
Moreover, embedding AI chipsets in connectivity modules can save space and simplify the form factor of IoT devices. In short, these modules are evolving from mere data communication facilitators to intelligent edge nodes capable of independently processing workloads.
For example, Guanghetong’s smart mowing robot solution is a typical application of AI cellular IoT modules. It uses Qualcomm’s smart module to achieve powerful on-device computing, capable of not only mapping the environment and avoiding obstacles but also economically and efficiently identifying mowing areas without continuous cloud connectivity. This fully demonstrates the practical value of AI chipsets in IoT devices.
Chuangtong Lianda’s EB3G2 IoT edge gateway utilizes Qualcomm SoC to execute AI models on devices. This SoC enables instant data analysis, reducing latency and cloud dependency. The built-in algorithms of the gateway can perform human detection and tracking, benefiting scenarios such as security and traffic management.
The Future of Communication, Perception, Intelligence, and Value Integration: Ubiquitous Intelligence, Ultimate Experience, and Ecological Co-prosperity
As edge intelligence continues to develop and cellular IoT modules upgrade, the integration of communication, perception, intelligence, and value is ushering in broader development prospects. In the future, we expect to see ubiquitous intelligence, ultimate experiences, and ecological co-prosperity become the main themes in this field.
1. Ubiquitous Intelligence: Comprehensive Intelligence from Perception to Decision
In the future, the integration of communication, perception, intelligence, and value will achieve comprehensive intelligence from perception to decision. Thanks to advancements in technologies like Tiny AI, more traditional sensors and devices will possess micro-edge AI capabilities, capable of performing preliminary data analysis and decision-making locally, truly realizing “intelligent perception.”
At the same time, with the support of dedicated chips like NPUs on the thin and thick edge sides, the speed and efficiency of AI inference and training will be further enhanced, promoting the implementation of more complex AI applications. As AI capabilities continue to sink to the edge side, future communication, perception, intelligence, and value systems will exhibit characteristics of ubiquitous intelligence, present everywhere and at all times.
2. Ultimate Experience: Real-time Response, Efficient Collaboration for User Experience
Another important development direction for the integration of communication, perception, intelligence, and value is to bring users an ultimate experience characterized by real-time response and efficient collaboration. Currently, edge intelligence can significantly reduce data transmission latency, but it still struggles to meet the stringent requirements of latency-sensitive applications such as industrial metaverse and autonomous driving.
In the future, by introducing new-generation communication technologies like 5G/6G and further upgrading the computing and storage architecture on the edge side, the end-to-end latency is expected to be reduced to milliseconds or even microseconds, achieving truly real-time interaction.
Additionally, as the collaborative capabilities of heterogeneous computing power continue to enhance, intelligent devices at different levels will be able to collaborate more efficiently, providing a seamless immersive experience.
3. Ecological Co-prosperity: Open Integration, Multi-win Development Pattern
As the ecosystem of communication, perception, intelligence, and value integration matures, open integration and multi-win will become the main theme of the industry. On one hand, the rise of open-source software and hardware platforms will accelerate the popularization and iteration of edge intelligence technologies, allowing more SMEs and innovative teams to participate in ecosystem construction.
On the other hand, cross-industry integration will become the norm, with chip manufacturers, device manufacturers, telecom operators, software service providers, and other parties in the industry chain strengthening cooperation, fully leveraging their respective advantages to jointly promote the healthy development of the industry.
Moreover, the innovative integration of edge intelligence with technologies like cloud computing and blockchain will also give rise to more new application scenarios and business models, injecting new vitality into the integration of communication, perception, intelligence, and value.
In summary, the integration of communication, perception, intelligence, and value is at a critical stage of transformation from quantitative change to qualitative change. As trends such as ubiquitous intelligence, ultimate experience, and ecological co-prosperity continue to deepen, edge intelligence will enter a new stage of development.
Final Thoughts
Throughout this article, we can easily see that the integration of communication, perception, intelligence, and value is reshaping the development pattern of the intelligent IoT at an unprecedented speed and breadth.
From the cloud to the edge, from perception to decision, from chips to modules, from algorithms to applications, intelligence is permeating and reconstructing every aspect of the IoT. All of this heralds the arrival of a new era.
In this era, the edge is no longer a subordinate of the cloud but an important carrier and source of intelligence; perception is no longer blind data collection but a wise behavior with analysis and decision-making capabilities; connection is no longer simple data transmission but a bond of intelligent collaboration and integration. Communication, intelligence, and value are deeply intertwined, weaving together a global intelligent IoT 2.0 network.
References:Apple’s Jony Ive and OpenAI’s Sam Altman seek funds for new AI personal device, Author: Rachael Davies, Source: readwrite.com The AI Hardware Dilemma – Why new devices are flopping – and how they might succeed, Author: EVAN ARMSTRONG, Source: every.to The top 6 edge AI trends—as showcased at Embedded World 2024, Source: IoT Analytics
Selected Articles


